Textbook Question
(a) Draw Lewis structures for chloromethane 1CH3Cl2, chloroethene 1C2H3Cl2, and chloroethyne 1C2HCl2. Draw Lewis structures for chloromethane 1CH3Cl2.
322
views
 Brown 14th Edition
Brown 14th Edition Ch.24 - The Chemistry of Life: Organic and Biological Chemistry
Ch.24 - The Chemistry of Life: Organic and Biological Chemistry Problem 83
Problem 83 Verified step by step guidance
Verified step by step guidance
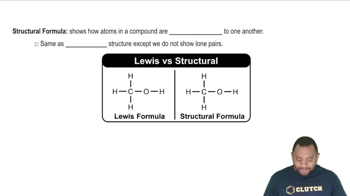


(a) Draw Lewis structures for chloromethane 1CH3Cl2, chloroethene 1C2H3Cl2, and chloroethyne 1C2HCl2. Draw Lewis structures for chloromethane 1CH3Cl2.
(a) Draw Lewis structures for chloromethane 1CH3Cl2, chloroethene 1C2H3Cl2, and chloroethyne 1C2HCl2. Draw Lewis structures for chloroethene 1C2H3Cl2.
(a) Draw Lewis structures for chloromethane 1CH3Cl2, chloroethene 1C2H3Cl2, and chloroethyne 1C2HCl2. Draw Lewis structures for chloroethyne 1C2HCl2.