Open Question
A hard water sample contains 0.0085% Ca by mass (in the form of Ca2+ ions). How much water (in grams) contains 1.2 g of Ca? (1.2 g of Ca is the recommended daily allowance of calcium for adults between 19 and 24 years old.)
 Verified step by step guidance
Verified step by step guidance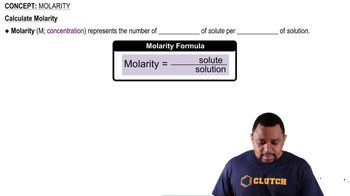


Lead is a toxic metal that affects the central nervous system. A Pb-contaminated water sample contains 0.0011% Pb by mass. How much of the water (in mL) contains 150 mg of Pb? (Assume a density of 1.0 g/mL.)
Describe how to prepare each solution from the dry solute and the solvent. b. 125 g of 0.100 m NaNO3
Describe how to prepare each solution from the dry solute and the solvent. c. 125 g of 1.0% NaNO3 solution by mass