Here are the essential concepts you must grasp in order to answer the question correctly.
Corrosion Mechanism
Corrosion is the process by which metals deteriorate due to chemical reactions with their environment, often involving oxidation. In metals, this can lead to the formation of rust or other oxides that weaken the material. Understanding the specific reactions that occur in different environments is crucial for comparing the corrosion resistance of materials.
Recommended video:
Reaction Mechanism Overview
Oxide Ceramics Structure
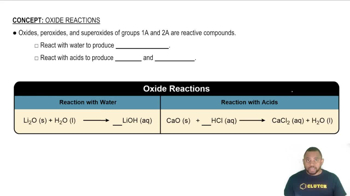
Oxide ceramics are inorganic, non-metallic materials characterized by their crystalline structure and strong ionic or covalent bonds. This structure provides them with high stability and resistance to chemical attack, making them less susceptible to corrosion compared to metals, which often have weaker metallic bonds that can be easily disrupted.
Recommended video:
Thermodynamic Stability
Thermodynamic stability refers to the tendency of a material to maintain its structure and composition under varying environmental conditions. Oxide ceramics typically have higher thermodynamic stability than metals, meaning they are less likely to undergo phase changes or chemical reactions that lead to degradation, thus enhancing their corrosion resistance.
Recommended video:
First Law of Thermodynamics
 Verified step by step guidance
Verified step by step guidance