Here are the essential concepts you must grasp in order to answer the question correctly.
Electrolytes
Electrolytes are substances that dissociate into ions when dissolved in water, allowing the solution to conduct electricity. Sodium acetate, a strong electrolyte, completely dissociates into sodium (Na+) and acetate (CH3CO2-) ions in solution. Understanding the behavior of electrolytes is crucial for calculating properties like pH and colligative effects, which are relevant to the freezing point of the solution.
Recommended video:
Electrolytes and Strong Acids
pH and Acid-Base Chemistry
pH is a measure of the acidity or basicity of a solution, defined as the negative logarithm of the hydrogen ion concentration. A pH of 9.07 indicates a basic solution, which can affect the dissociation of weak acids and bases. In the case of sodium acetate, the acetate ion can act as a weak base, influencing the overall pH and the calculations related to the solution's properties.
Recommended video:
pH of Strong Acids and Bases
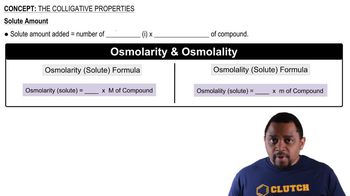
Colligative Properties
Colligative properties are physical properties of solutions that depend on the number of solute particles in a given amount of solvent, rather than the identity of the solute. These properties include boiling point elevation and freezing point depression. To determine the freezing point of the sodium acetate solution, one must calculate its molality, which is essential for applying the freezing point depression formula.
Recommended video: