Here are the essential concepts you must grasp in order to answer the question correctly.
First-Order Reactions
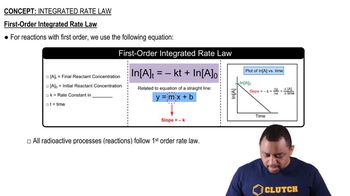
First-order reactions are chemical reactions where the rate is directly proportional to the concentration of one reactant. In this case, the rate of cyclopropane's reaction is dependent solely on its concentration. The integrated rate law for a first-order reaction can be expressed as ln([A]0/[A]) = kt, where [A]0 is the initial concentration, [A] is the concentration at time t, k is the rate constant, and t is time.
Recommended video:
Rate Constant
The rate constant (k) is a proportionality factor in the rate law that provides insight into the speed of a reaction. It varies with temperature and is specific to each reaction. In this scenario, the rate constant is given as 5.87 * 10^-4 s^-1 at 485 °C, indicating how quickly cyclopropane reacts under these conditions. A higher rate constant signifies a faster reaction.
Recommended video:
Partial Pressure
Partial pressure is the pressure exerted by a single component of a gas mixture. It is crucial in understanding gas reactions, as the total pressure is the sum of the partial pressures of all gases present. In this question, the initial partial pressure of cyclopropane is 722 torr, and the goal is to determine the time required for it to decrease to below 100 torr, which involves applying the first-order kinetics to the change in pressure over time.
Recommended video:
Partial Pressure Calculation