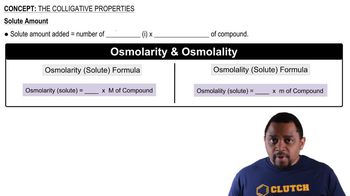
Here are the essential concepts you must grasp in order to answer the question correctly.
Colligative Properties
Colligative properties are physical properties of solutions that depend on the number of solute particles in a given amount of solvent, rather than the identity of the solute. These properties include boiling point elevation and freezing point depression, which are crucial for understanding how solutes affect the phase changes of solvents.
Recommended video:
Dissociation of Ionic Compounds
Ionic compounds, such as sodium nitrate (NaNO3), dissociate into their constituent ions when dissolved in water. For NaNO3, it dissociates into Na+ and NO3- ions. This dissociation increases the total number of solute particles in the solution, which directly influences the colligative properties.
Recommended video:
Freezing Point Depression and Boiling Point Elevation Formulas
The freezing point depression and boiling point elevation can be calculated using the formulas ΔTf = i * Kf * m and ΔTb = i * Kb * m, where ΔTf and ΔTb are the changes in freezing and boiling points, respectively, i is the van 't Hoff factor (number of particles the solute dissociates into), Kf and Kb are the solvent's freezing and boiling point constants, and m is the molality of the solution.
Recommended video:
Freezing Point Depression
 Verified step by step guidance
Verified step by step guidance