Here are the essential concepts you must grasp in order to answer the question correctly.
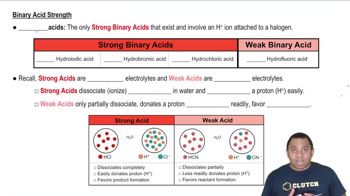
Acid Strength
Acid strength refers to the ability of an acid to donate protons (H⁺ ions) in solution. Strong acids completely dissociate in water, releasing all their protons, while weak acids only partially dissociate. The strength of an acid is often determined by its dissociation constant (Ka), with larger values indicating stronger acids.
Recommended video:
Molecular Structure and Polarity
The molecular structure and polarity of an acid influence its strength. Acids with highly electronegative atoms or groups can stabilize the negative charge of the conjugate base after proton donation, making them stronger. The arrangement of atoms and the presence of electronegative elements can affect the acid's ability to release protons.
Recommended video:
Comparative Analysis of Acids
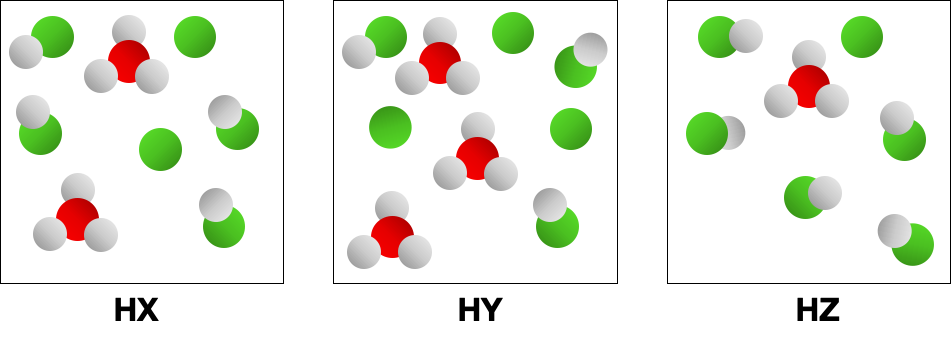
To determine which acid is the strongest among several, a comparative analysis of their structures and dissociation behaviors is necessary. This involves examining factors such as bond strength, electronegativity, and the stability of the resulting conjugate bases. By evaluating these characteristics, one can predict which acid will more readily donate protons in solution.
Recommended video:
Comparing Binary Acid Strength
 Verified step by step guidance
Verified step by step guidance