 McMurry 8th Edition
McMurry 8th Edition Ch.18 - Thermodynamics: Entropy, Free Energy & Equilibrium
Ch.18 - Thermodynamics: Entropy, Free Energy & Equilibrium Problem 16
Problem 16Chapter 18, Problem 16
Consider the following graph of total free energy of reactants and products versus reaction progress for the general reaction, Reactants -> Products. At which of the four points (labeled a, b, c, and d) is Q < K?
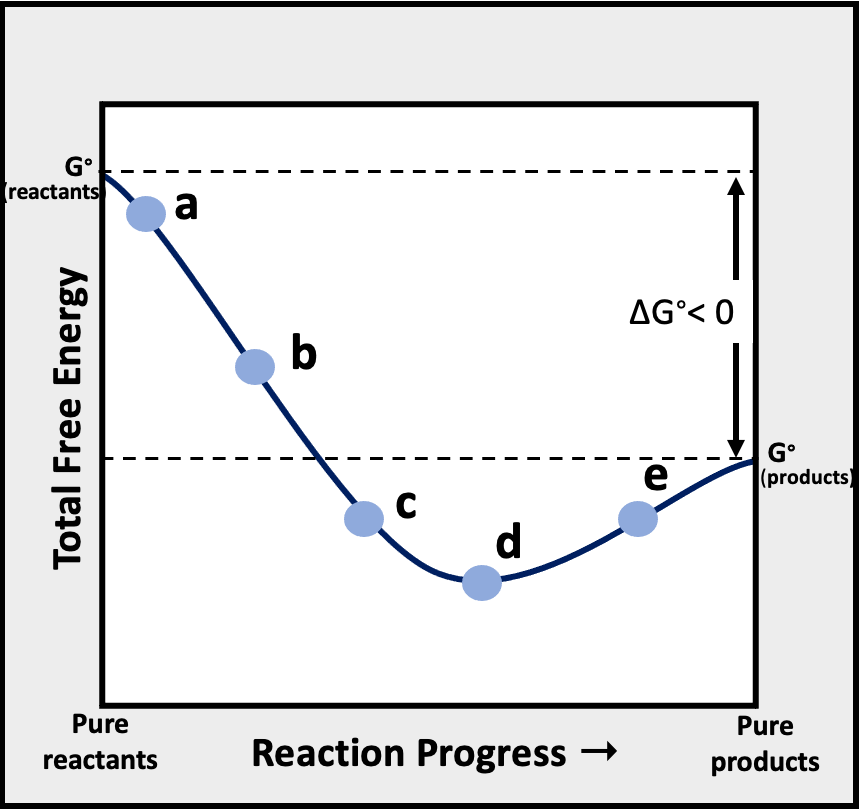
 Verified Solution
Verified SolutionVideo transcript
Spinach contains a lot of iron but is not a good source of dietary iron because nearly all the iron is tied up in the oxalate complex [Fe(C2O4)3]3-.
(b) Under the acidic conditions in the stomach, the Fe3+ concentration should be greater because of the reaction
[Fe(C2O4)3]3-(aq) + 6 H3O+(aq) ⇌ Fe3+(aq) + 3 H2C2O4(aq) + 6 H2O(l)
Show, however, that this reaction is nonspontaneous under standard-state conditions. (For H2C2O4, Ka1 = 5.9 × 10-2 and Ka2 = 6.4 × 10-5.)
Formation constants for the ammonia and ethylenediamine complexes of nickel(II) indicate that Ni(en)32+ is much more
stable than Ni(NH3)62+:
(1) <REACTION>
(2) <REACTION>
The enthalpy changes for the two reactions, ΔH°1 and ΔH°2, should be about the same because both complexes have six Ni﹣N bonds.
(c) Assuming that ΔH°2 - ΔH°1 is zero, calculate the value of ΔS°2 - ΔS°1.