The structural formulas of the compounds n-butane and isobutane are shown below. (b) Determine the empirical formula of each.

 Verified step by step guidance
Verified step by step guidance
Verified Solution
Key Concepts
Empirical Formula

Structural Formulas
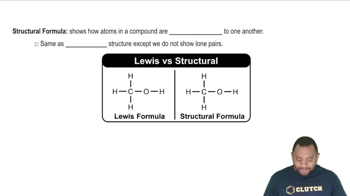
Isomers

For each of the following elements, write its chemical symbol, determine the name of the group to which it belongs (Table 2.3), and indicate whether it is a metal, metalloid, or nonmetal: (a) polonium (b) strontium (c) neon (d) rubidium (e) sulfur.
The structural formulas of the compounds n-butane and isobutane are shown below. (c) Which formulas—empirical, molecular, or structural—allow you determine these are different compounds?
Ball-and-stick representations of benzene, a colorless liquid often used in organic chemistry reactions, and acetylene, a gas used as a fuel for high-temperature welding, are shown below. (a) Determine the molecular formula of each.
What are the molecular and empirical formulas for each of the following compounds? Write the molecular formula for the following compound.
