Here are the essential concepts you must grasp in order to answer the question correctly.
Colligative Properties
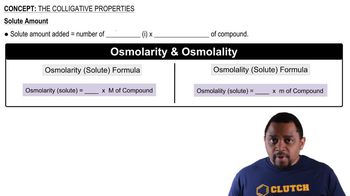
Colligative properties are physical properties of solutions that depend on the number of solute particles in a given amount of solvent, rather than the identity of the solute. These properties include boiling point elevation and freezing point depression, which are crucial for calculating the changes in freezing and boiling points when a solute is added to a solvent.
Recommended video:
Molar Mass and Mole Calculation
To calculate the effects of a solute on the freezing and boiling points, it is essential to determine the molar mass of the solute and convert grams to moles. For naphthalene (C10H8), the molar mass is approximately 128.17 g/mol, which allows for the calculation of the number of moles present in the solution, a key step in applying colligative property formulas.
Recommended video:
Molar Mass Calculation Example
Freezing Point Depression and Boiling Point Elevation Formulas
The freezing point depression and boiling point elevation can be calculated using the formulas ΔTf = i * Kf * m and ΔTb = i * Kb * m, where ΔTf and ΔTb are the changes in freezing and boiling points, respectively, i is the van 't Hoff factor (which is 1 for naphthalene), Kf and Kb are the solvent's freezing and boiling point constants, and m is the molality of the solution. These formulas are essential for determining the new freezing and boiling points of the solution.
Recommended video:
Freezing Point Depression