Here are the essential concepts you must grasp in order to answer the question correctly.
Linear Equations
A linear equation is an algebraic expression that represents a straight line when graphed. It typically takes the form ax + b = c, where a, b, and c are constants, and x is the variable. Solving a linear equation involves isolating the variable on one side of the equation to find its value.
Recommended video:
Categorizing Linear Equations
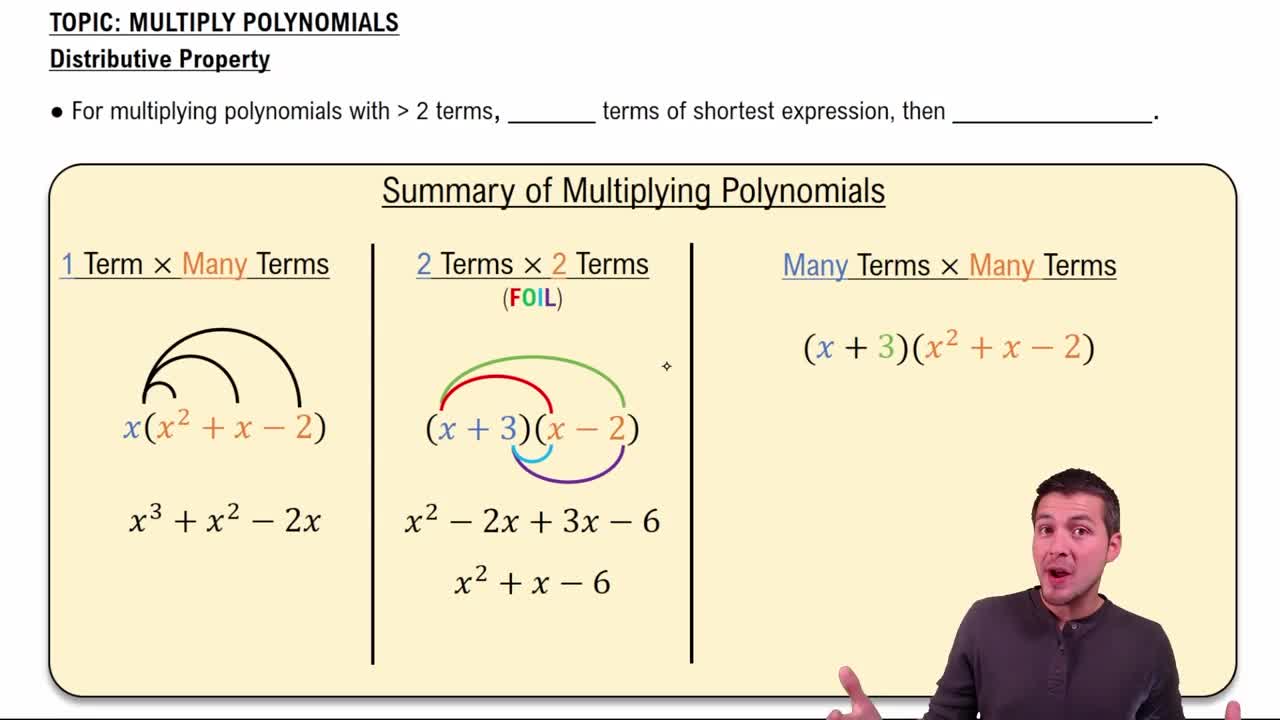
Distributive Property
The distributive property states that a(b + c) = ab + ac, allowing us to multiply a single term by two or more terms inside parentheses. This property is essential for simplifying expressions and solving equations, as it helps eliminate parentheses and combine like terms effectively.
Recommended video:
Multiply Polynomials Using the Distributive Property
Checking Solutions
Checking solutions involves substituting the found value of the variable back into the original equation to verify its correctness. This step ensures that the solution satisfies the equation, confirming that no errors occurred during the solving process. It is a crucial part of problem-solving in algebra.
Recommended video:
Restrictions on Rational Equations
 Verified step by step guidance
Verified step by step guidance