Here are the essential concepts you must grasp in order to answer the question correctly.
Linear Equations
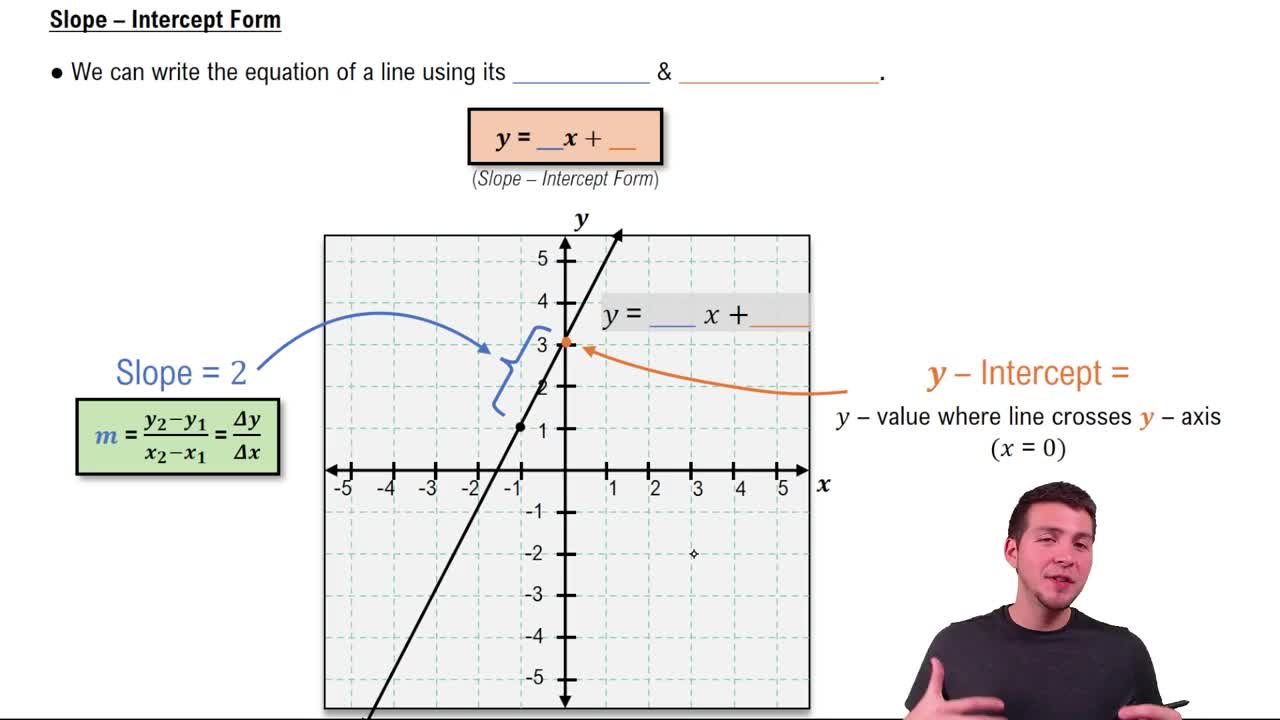
A linear equation is an algebraic expression that represents a straight line when graphed on a coordinate plane. It typically takes the form y = mx + b, where m is the slope and b is the y-intercept. In the given equation y = x + 2, the slope is 1, indicating that for every unit increase in x, y increases by the same amount.
Recommended video:
Categorizing Linear Equations
Graphing Points
Graphing points involves plotting specific coordinates on a Cartesian plane, where the x-coordinate represents the horizontal position and the y-coordinate represents the vertical position. For the equation y = x + 2, you can calculate y for each given x value (-3, -2, -1, 0, 1, 2, 3) to find corresponding points, which can then be plotted to visualize the linear relationship.
Recommended video:
Graphing Equations of Two Variables by Plotting Points
Slope-Intercept Form
The slope-intercept form of a linear equation is expressed as y = mx + b, where m is the slope and b is the y-intercept. This form is particularly useful for quickly identifying the slope and y-intercept of a line, allowing for easy graphing. In the equation y = x + 2, the slope is 1 and the y-intercept is 2, indicating that the line crosses the y-axis at (0, 2).
Recommended video:
 Verified step by step guidance
Verified step by step guidance