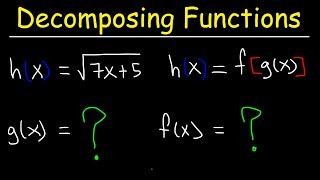
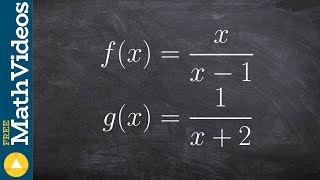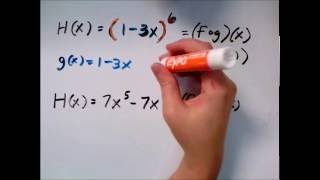3. Functions
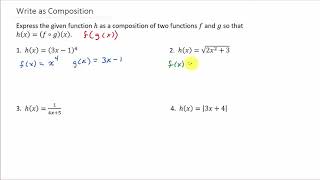
Function Composition
3. Functions
Function Composition
Additional 2 creators.
Learn with other creators
Showing 5 of 5 videos
Practice this topic
- Multiple Choice
Given the functions and find and
756views6rank2comments - Multiple Choice
Given the functions and find and .
670views - Multiple Choice
Given the functions and find and .
716views3rank - Multiple Choice
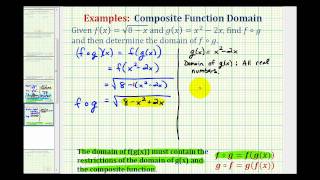
Given the functions and find and determine its domain.
695views1rank - Textbook Question
Find the domain of each function. f(x) = 2(x+5)
680views - Textbook Question
Find the domain of each function. g(x) = 3/(x-4)
627views - Textbook Question
Without using paper and pencil, evaluate each expression given the following functions. and
(ƒg)(2)
724views - Textbook Question
Find the domain of each function. g(x) = 2/(x+5)
690views