Table of contents
- 0. Review of Algebra4h 16m
- 1. Equations & Inequalities3h 18m
- 2. Graphs of Equations43m
- 3. Functions2h 17m
- 4. Polynomial Functions1h 44m
- 5. Rational Functions1h 23m
- 6. Exponential & Logarithmic Functions2h 28m
- 7. Systems of Equations & Matrices4h 6m
- 8. Conic Sections2h 23m
- 9. Sequences, Series, & Induction1h 19m
- 10. Combinatorics & Probability1h 45m
7. Systems of Equations & Matrices
Graphing Systems of Inequalities
Problem 61
Textbook Question
Textbook QuestionIn Exercises 27–62, graph the solution set of each system of inequalities or indicate that the system has no solution. 3x+y≤6, 2x−y≤−1, x>−2, y<4
 Verified Solution
Verified SolutionThis video solution was recommended by our tutors as helpful for the problem above
Video duration:
9mPlay a video:
Was this helpful?
Key Concepts
Here are the essential concepts you must grasp in order to answer the question correctly.
Inequalities
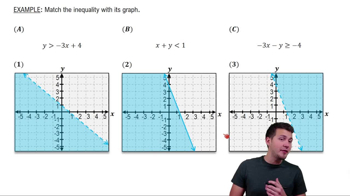
Inequalities are mathematical expressions that show the relationship between two values when they are not equal. They use symbols such as ≤ (less than or equal to), ≥ (greater than or equal to), < (less than), and > (greater than). Understanding how to interpret and manipulate inequalities is crucial for solving systems of inequalities, as it allows us to determine the regions of the coordinate plane that satisfy the given conditions.
Recommended video:

Linear Inequalities
Graphing Systems of Inequalities
Graphing systems of inequalities involves plotting each inequality on a coordinate plane to visualize the solution set. Each inequality divides the plane into two regions, and the solution set is where these regions overlap. It is important to use dashed lines for inequalities that do not include equality (like < or >) and solid lines for those that do (like ≤ or ≥). This graphical representation helps in identifying feasible solutions.
Recommended video:
Guided course

Systems of Inequalities
Feasible Region
The feasible region is the area on a graph where all the inequalities in a system are satisfied simultaneously. It is typically bounded by the lines representing the inequalities and can be unbounded in some cases. Identifying the feasible region is essential for understanding the solutions to the system, as it visually represents all possible combinations of variable values that meet the criteria set by the inequalities.
Recommended video:

Probability of Non-Mutually Exclusive Events Example

 7:2m
7:2mWatch next
Master Linear Inequalities with a bite sized video explanation from Patrick Ford
Start learning