Table of contents
- 0. Functions7h 52m
- Introduction to Functions16m
- Piecewise Functions10m
- Properties of Functions9m
- Common Functions1h 8m
- Transformations5m
- Combining Functions27m
- Exponent rules32m
- Exponential Functions28m
- Logarithmic Functions24m
- Properties of Logarithms34m
- Exponential & Logarithmic Equations35m
- Introduction to Trigonometric Functions38m
- Graphs of Trigonometric Functions44m
- Trigonometric Identities47m
- Inverse Trigonometric Functions48m
- 1. Limits and Continuity2h 2m
- 2. Intro to Derivatives1h 33m
- 3. Techniques of Differentiation3h 18m
- 4. Applications of Derivatives2h 38m
- 5. Graphical Applications of Derivatives6h 2m
- 6. Derivatives of Inverse, Exponential, & Logarithmic Functions2h 37m
- 7. Antiderivatives & Indefinite Integrals1h 26m
- 8. Definite Integrals4h 44m
- 9. Graphical Applications of Integrals2h 27m
- 10. Physics Applications of Integrals 2h 22m
4. Applications of Derivatives
Differentials
Problem 4.8.3
Textbook Question
A graph of ƒ and the lines tangent to ƒ at x = 1, 2 and 3 are given. If x₀ = 3, find the values of x₁, x₂, and x₃, that are obtained by applying Newton’s method. <IMAGE>
 Verified step by step guidance
Verified step by step guidance1
Understand Newton's Method: Newton's method is an iterative process used to find successively better approximations to the roots (or zeroes) of a real-valued function. The formula for Newton's method is: x_{n+1} = x_n - \frac{f(x_n)}{f'(x_n)}.
Identify the initial guess: In this problem, the initial guess x₀ is given as 3. This is the starting point for applying Newton's method.
Calculate f(x₀) and f'(x₀): To apply Newton's method, you need the value of the function f at x₀ and the value of its derivative f' at x₀. Use the graph or any given information to determine these values.
Apply Newton's formula: Use the values obtained in the previous step to calculate x₁ using the formula x₁ = x₀ - \frac{f(x₀)}{f'(x₀)}. This will give you the next approximation.
Repeat the process: Use x₁ as the new approximation and repeat the process to find x₂ and x₃. For each step, calculate f(x_n) and f'(x_n), then apply the formula x_{n+1} = x_n - \frac{f(x_n)}{f'(x_n)} to find the next approximation.
 Verified video answer for a similar problem:
Verified video answer for a similar problem:This video solution was recommended by our tutors as helpful for the problem above
Video duration:
2mPlay a video:
Was this helpful?
Key Concepts
Here are the essential concepts you must grasp in order to answer the question correctly.
Newton's Method
Newton's Method is an iterative numerical technique used to find approximate solutions to equations. It starts with an initial guess and refines it using the formula x_{n+1} = x_n - f(x_n)/f'(x_n), where f is the function and f' is its derivative. This method is particularly effective for finding roots of functions and converges quickly under suitable conditions.
Recommended video:
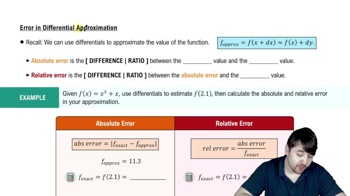
Evaluating Composed Functions
Tangent Lines
A tangent line to a function at a given point represents the instantaneous rate of change of the function at that point. It is defined by the slope, which is the derivative of the function at that point. In the context of Newton's Method, the tangent line at the current approximation provides a linear approximation of the function, guiding the next iteration towards the root.
Recommended video:
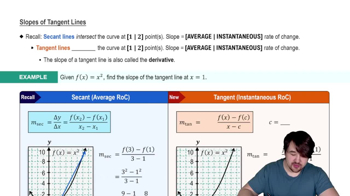
Slopes of Tangent Lines
Derivatives
The derivative of a function measures how the function's output changes as its input changes, essentially representing the slope of the function at any given point. It is a fundamental concept in calculus that allows us to analyze the behavior of functions, including identifying local maxima and minima, and is crucial for applying Newton's Method effectively.
Recommended video:

Derivatives