Table of contents
- 0. Functions7h 52m
- Introduction to Functions16m
- Piecewise Functions10m
- Properties of Functions9m
- Common Functions1h 8m
- Transformations5m
- Combining Functions27m
- Exponent rules32m
- Exponential Functions28m
- Logarithmic Functions24m
- Properties of Logarithms34m
- Exponential & Logarithmic Equations35m
- Introduction to Trigonometric Functions38m
- Graphs of Trigonometric Functions44m
- Trigonometric Identities47m
- Inverse Trigonometric Functions48m
- 1. Limits and Continuity2h 2m
- 2. Intro to Derivatives1h 33m
- 3. Techniques of Differentiation3h 18m
- 4. Applications of Derivatives2h 38m
- 5. Graphical Applications of Derivatives6h 2m
- 6. Derivatives of Inverse, Exponential, & Logarithmic Functions2h 37m
- 7. Antiderivatives & Indefinite Integrals1h 26m
- 8. Definite Integrals3h 25m
3. Techniques of Differentiation
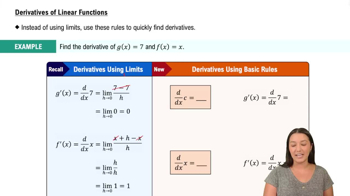
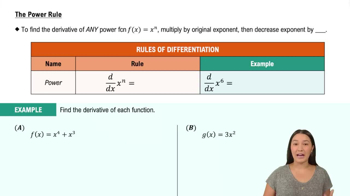
Basic Rules of Differentiation
Problem 91b
Textbook Question
If possible, evaluate the following derivatives using the graphs of f and f'. <IMAGE>
b. (f^-1)'(3)
 Verified step by step guidance
Verified step by step guidance1
Understand the problem: We need to find the derivative of the inverse function at a specific point, (f^-1)'(3). This involves using the relationship between a function and its inverse.
Recall the formula for the derivative of an inverse function: If y = f(x) and f is invertible, then the derivative of the inverse function at a point is given by (f^-1)'(y) = 1 / f'(x), where x = f^-1(y).
Identify the point on the graph: We need to find the x-value such that f(x) = 3. This means we are looking for the x-coordinate where the function f has a value of 3.
Use the graph of f to find the x-value: Locate the point on the graph of f where the y-coordinate is 3. This x-value will be used in the formula for the derivative of the inverse function.
Evaluate the derivative using the graph of f': Once the x-value is found, use the graph of f' to determine f'(x). Then, apply the formula (f^-1)'(3) = 1 / f'(x) to find the derivative of the inverse function at the point.
 Verified video answer for a similar problem:
Verified video answer for a similar problem:This video solution was recommended by our tutors as helpful for the problem above
Video duration:
3mPlay a video:
Was this helpful?
Key Concepts
Here are the essential concepts you must grasp in order to answer the question correctly.
Inverse Function Theorem
The Inverse Function Theorem states that if a function f is continuous and differentiable, and its derivative f' is non-zero at a point, then the inverse function f^-1 exists locally around that point. This theorem provides a way to find the derivative of the inverse function using the formula (f^-1)'(y) = 1 / f'(f^-1(y)), which is essential for evaluating derivatives of inverse functions.
Recommended video:

Inverse Cosine
Derivative of a Function
The derivative of a function measures the rate at which the function's value changes as its input changes. It is defined as the limit of the average rate of change of the function over an interval as the interval approaches zero. Understanding how to compute and interpret derivatives is crucial for analyzing the behavior of functions and their inverses.
Recommended video:

Derivatives of Other Trig Functions
Graphical Interpretation of Derivatives
The graphical interpretation of derivatives involves understanding how the slope of the tangent line to the graph of a function at a given point represents the derivative at that point. For inverse functions, the slopes of the original function and its inverse are reciprocals at corresponding points, which is a key concept when evaluating derivatives using graphs.
Recommended video:

Graphical Applications of Exponential & Logarithmic Derivatives: Example 8

 3:59m
3:59mWatch next
Master Derivatives of Linear Functions with a bite sized video explanation from Callie
Start learningRelated Videos
Related Practice