Table of contents
- 0. Functions7h 52m
- Introduction to Functions16m
- Piecewise Functions10m
- Properties of Functions9m
- Common Functions1h 8m
- Transformations5m
- Combining Functions27m
- Exponent rules32m
- Exponential Functions28m
- Logarithmic Functions24m
- Properties of Logarithms34m
- Exponential & Logarithmic Equations35m
- Introduction to Trigonometric Functions38m
- Graphs of Trigonometric Functions44m
- Trigonometric Identities47m
- Inverse Trigonometric Functions48m
- 1. Limits and Continuity2h 2m
- 2. Intro to Derivatives1h 33m
- 3. Techniques of Differentiation3h 18m
- 4. Applications of Derivatives2h 38m
- 5. Graphical Applications of Derivatives6h 2m
- 6. Derivatives of Inverse, Exponential, & Logarithmic Functions2h 37m
- 7. Antiderivatives & Indefinite Integrals1h 26m
- 8. Definite Integrals4h 44m
- 9. Graphical Applications of Integrals2h 27m
- 10. Physics Applications of Integrals 2h 22m
4. Applications of Derivatives
Motion Analysis
Problem 3.6.38a
Textbook Question
Comparing velocities Two stones are thrown vertically upward, each with an initial velocity of 48 ft/s at time t=0. One stone is thrown from the edge of a bridge that is 32 feet above the ground, and the other stone is thrown from ground level. The height above the ground of the stone thrown from the bridge after t seconds is f(t) = − 16t²+48t+32. and the height of the stone thrown from the ground after t seconds is g(t) = −16t²+48t.
a. Show that the stones reach their high points at the same time.
 Verified step by step guidance
Verified step by step guidance1
Identify the height functions for both stones: f(t) = -16t² + 48t + 32 for the stone thrown from the bridge, and g(t) = -16t² + 48t for the stone thrown from the ground.
To find the time at which each stone reaches its highest point, we need to determine the vertex of the parabolic functions f(t) and g(t). The vertex form of a parabola given by ax² + bx + c is at t = -b/(2a).
For both functions, f(t) and g(t), the coefficient a is -16 and the coefficient b is 48. Substitute these values into the vertex formula: t = -48/(2 * -16).
Calculate the expression t = -48/(2 * -16) to find the time at which both stones reach their maximum height.
Since both functions have the same coefficients for t² and t, the time at which they reach their maximum height is the same for both stones.
 Verified video answer for a similar problem:
Verified video answer for a similar problem:This video solution was recommended by our tutors as helpful for the problem above
Video duration:
3mPlay a video:
Was this helpful?
Key Concepts
Here are the essential concepts you must grasp in order to answer the question correctly.
Quadratic Functions
The height functions f(t) and g(t) are quadratic equations, which are polynomial functions of degree two. They can be expressed in the standard form f(t) = at² + bt + c, where 'a', 'b', and 'c' are constants. The graph of a quadratic function is a parabola, and its vertex represents the maximum or minimum point, which is crucial for determining the high point of the stones.
Recommended video:
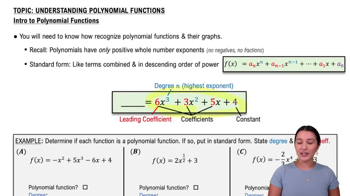
Introduction to Polynomial Functions
Vertex of a Parabola
The vertex of a parabola given by a quadratic function occurs at the time t = -b/(2a), where 'a' and 'b' are the coefficients from the standard form of the quadratic equation. This point represents the maximum height for the upward-thrown stones. By calculating the vertex for both height functions, we can determine if they reach their high points simultaneously.
Recommended video:
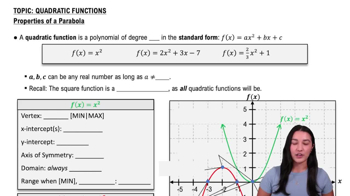
Properties of Parabolas
Initial Velocity and Gravity
In this scenario, both stones are thrown with an initial velocity of 48 ft/s, and the effect of gravity is modeled by the term -16t², which represents the downward acceleration due to gravity (in feet per second squared). Understanding how initial velocity and gravitational acceleration affect the motion of the stones is essential for analyzing their trajectories and determining when they reach their maximum heights.
Recommended video:

Initial Value Problems Example 2

 6:29m
6:29mWatch next
Master Derivatives Applied To Velocity with a bite sized video explanation from Nick
Start learning




