Table of contents
- 0. Functions7h 52m
- Introduction to Functions16m
- Piecewise Functions10m
- Properties of Functions9m
- Common Functions1h 8m
- Transformations5m
- Combining Functions27m
- Exponent rules32m
- Exponential Functions28m
- Logarithmic Functions24m
- Properties of Logarithms34m
- Exponential & Logarithmic Equations35m
- Introduction to Trigonometric Functions38m
- Graphs of Trigonometric Functions44m
- Trigonometric Identities47m
- Inverse Trigonometric Functions48m
- 1. Limits and Continuity2h 2m
- 2. Intro to Derivatives1h 33m
- 3. Techniques of Differentiation3h 18m
- 4. Applications of Derivatives2h 38m
- 5. Graphical Applications of Derivatives6h 2m
- 6. Derivatives of Inverse, Exponential, & Logarithmic Functions2h 37m
- 7. Antiderivatives & Indefinite Integrals1h 26m
- 8. Definite Integrals4h 44m
- 9. Graphical Applications of Integrals2h 27m
- 10. Physics Applications of Integrals 2h 22m
5. Graphical Applications of Derivatives
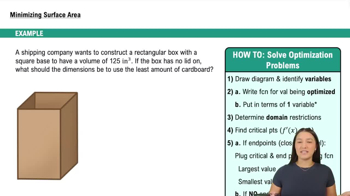
Applied Optimization
Problem 4.5.51
Textbook Question
Viewing angles An auditorium with a flat floor has a large screen on one wall. The lower edge of the screen is 3 ft above eye level and the upper edge of the screen is 10 ft above eye level (see figure). How far from the screen should you stand to maximize your viewing angle? <IMAGE>
 Verified step by step guidance
Verified step by step guidance1
First, define the viewing angle θ as the angle subtended by the screen at the viewer's eye level. This angle can be expressed in terms of the distances from the viewer to the lower and upper edges of the screen.
Next, use trigonometry to express the viewing angle θ in terms of the distance x from the screen. The tangent of the angle θ can be expressed as the difference in height of the screen divided by the distance x: tan(θ) = (10 - 3) / x.
To maximize the viewing angle, you need to find the value of x that maximizes θ. This involves taking the derivative of θ with respect to x and setting it equal to zero to find critical points.
Calculate the derivative of tan(θ) with respect to x, which involves using the chain rule and the derivative of the tangent function. Set this derivative equal to zero to solve for x.
Finally, verify that the critical point found is indeed a maximum by using the second derivative test or analyzing the behavior of the function around the critical point.
 Verified video answer for a similar problem:
Verified video answer for a similar problem:This video solution was recommended by our tutors as helpful for the problem above
Video duration:
12mPlay a video:
Was this helpful?
Key Concepts
Here are the essential concepts you must grasp in order to answer the question correctly.
Viewing Angle
The viewing angle is the angle formed between two lines drawn from the observer's eyes to the edges of an object, in this case, the screen. Maximizing this angle enhances the viewer's experience by allowing a broader perspective of the screen. Understanding how to calculate and optimize this angle is crucial for determining the ideal distance from the screen.
Recommended video:
Trig Values in Quadrants II, III, & IV Example 2
Trigonometric Functions
Trigonometric functions, such as tangent, sine, and cosine, relate the angles of a triangle to the lengths of its sides. In this scenario, the tangent function can be used to express the relationship between the height of the screen and the distance from the viewer to the screen. Mastery of these functions is essential for solving problems involving angles and distances.
Recommended video:

Introduction to Trigonometric Functions
Optimization
Optimization in calculus involves finding the maximum or minimum values of a function. In this context, we need to maximize the viewing angle by determining the optimal distance from the screen. This typically involves taking the derivative of the function representing the viewing angle and setting it to zero to find critical points.
Recommended video:

Intro to Applied Optimization: Maximizing Area

 1:13m
1:13mWatch next
Master Intro to Applied Optimization: Maximizing Area with a bite sized video explanation from Callie
Start learningRelated Videos
Related Practice