How do the phospholipids in archaea differ from those in other cells? a. They have tails made of unsaturated fatty acids instead of saturated fatty acids. b. They do not contain hydrocarbon chains. c. They have isoprenoid tails instead of fatty acid tails. d. They have two hydrocarbon chains instead of three hydrocarbon chains.
Ch. 6 - Lipids, Membranes, and the First Cells
Chapter 6, Problem 1
A cell is placed in a solution that is hypotonic to the cell. Which of the following best describes movement of water in this situation? a. Water will only flow into the cell. b. Water will only flow out of the cell. c. Water will flow into and out of the cell, but the overall net movement will be out of the cell. d. Water will flow into and out of the cell, but the overall net movement will be into the cell.
 Verified step by step guidance
Verified step by step guidance1
Understand the terms: A hypotonic solution has a lower concentration of solutes compared to the concentration inside the cell.
Recall osmosis: Osmosis is the movement of water across a semipermeable membrane from an area of lower solute concentration to an area of higher solute concentration.
Apply osmosis to the scenario: Since the solution is hypotonic relative to the cell, the water concentration outside the cell is higher than inside.
Predict water movement: Water will move from the hypotonic solution (higher water concentration) into the cell (lower water concentration) to try to equalize the solute concentrations on both sides of the membrane.
Choose the correct answer: The overall net movement of water will be into the cell, making option 'd' the correct answer.

Verified video answer for a similar problem:
This video solution was recommended by our tutors as helpful for the problem above.
Video duration:
2mWas this helpful?
Key Concepts
Here are the essential concepts you must grasp in order to answer the question correctly.
Osmosis
Osmosis is the movement of water molecules across a selectively permeable membrane from an area of lower solute concentration to an area of higher solute concentration. This process continues until equilibrium is reached, where the concentration of solutes is equal on both sides of the membrane. In biological systems, osmosis is crucial for maintaining cell turgor and overall homeostasis.
Recommended video:
Guided course
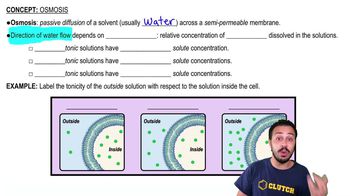
Osmosis
Hypotonic Solution
A hypotonic solution has a lower concentration of solutes compared to the inside of a cell. When a cell is placed in a hypotonic solution, water moves into the cell to balance the solute concentrations. This influx of water can cause the cell to swell and potentially burst if the osmotic pressure becomes too great.
Recommended video:
Guided course

Homogenous vs. Heterogenous Solutions
Net Movement of Water
The net movement of water refers to the overall direction of water flow across a membrane, taking into account both the inflow and outflow. In a hypotonic environment, while water may move in both directions, the net movement will be into the cell due to the higher concentration of solutes inside the cell, leading to an increase in cell volume.
Recommended video:
Guided course
Introduction to Water
Related Practice
Textbook Question
1268
views
Textbook Question
What is a fiber composite? How do cellular fiber composites resemble reinforced concrete?
1282
views
Textbook Question
If a solution surrounding a cell is hypertonic relative to the inside of the cell, how will water move? a. It will move into the cell via osmosis. b. It will move out of the cell via osmosis. c. It will not move, because equilibrium exists. d. It will evaporate from the cell surface more rapidly.
1344
views
Textbook Question
Where are protein components of the extracellular matrix synthesized? a. in the rough ER b. in the Golgi apparatus c. in the plasma membrane d. in the extracellular layer itself
1729
views
Textbook Question
What two conditions must be present for osmosis to occur?Integral membrane proteins are anchored in lipid bilayers.
1032
views
