<Image>
Mass strandings of whales occur on beaches near military exercises where sonar is used, raising concerns about the effects of human-generated underwater sounds on animal behavior. Scientists are collecting behavioral data on several species of whales to find out how sonar affects them.
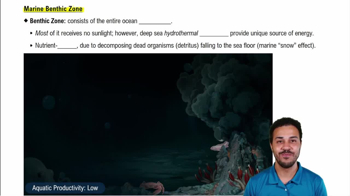
Researchers followed tagged blue whales to observe how they respond to simulated military sonar—using sound levels much lower than those typically used during military exercises. Analyze the sample of data below for one individual blue whale and summarize the behavioral effect of the sound exposure.