Temperate forest in China and temperate forest in North America are part of the same biome but are distinct ecosystems. Explain.

Scientists predict that global climate change will cause a greater increase in average temperature at higher latitudes than in the tropics. This seems like good news since most of the world's biodiversity occurs in the tropics. However, recent data suggest that a smaller temperature change in the tropics will cause a larger physiological response in organisms there than the larger temperature change will in organisms in temperate areas. Based on what you have learned about thermal niches in this chapter, propose a hypothesis to explain this result.
 Verified step by step guidance
Verified step by step guidance
Verified video answer for a similar problem:
Key Concepts
Thermal Niches
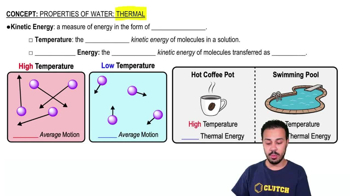
Physiological Response

Biodiversity and Climate Change

Compare the distribution of the natural terrestrial biomes of eastern North America with the distribution of anthropogenic biomes.
Like Earth, Mars has seasons—its Northern Hemisphere experiences winter when its Southern Hemisphere experiences summer. Which statement is the best explanation for seasonality on Mars?
a. Mars is tilted on its axis.
b. Mars has an elliptical orbit that brings it closer to the Sun in summer than in winter.
c. Mars has a circular orbit and maintains a constant distance from the Sun.
d. The Southern Hemisphere of Mars consistently receives direct solar radiation.
<Image?
The red lionfish, Pterois volitans, has beautiful red stripes, streaming fins, and a fearless disposition, and it is deadly. Native to the Pacific Ocean, the red lionfish was first discovered on coral reefs in the Bahamas in 1985. The species has spread to over 3 million square kilometers of the western Atlantic and Gulf of Mexico. Lionfish have a voracious appetite for native fish, are armed with venomous spines, and have no natural predators in their new range.
Why are species like the lionfish considered 'invasive'?
a. They are found in areas where they are not native.
b. They were accidentally introduced by humans.
c. They spread aggressively and displace native species.
d. They are predators of other fish.
<Image?
The red lionfish, Pterois volitans, has beautiful red stripes, streaming fins, and a fearless disposition, and it is deadly. Native to the Pacific Ocean, the red lionfish was first discovered on coral reefs in the Bahamas in 1985. The species has spread to over 3 million square kilometers of the western Atlantic and Gulf of Mexico. Lionfish have a voracious appetite for native fish, are armed with venomous spines, and have no natural predators in their new range.
Lionfish are usually found in full-salinity seawater (35 parts per thousand). However, lab studies show that lionfish can tolerate salinities as low as 4 parts per thousand for several days, suggesting that the low-salinity water of estuaries (such as at the mouth of the Amazon River) may not be a barrier to lionfish dispersal along the coasts. Sketch a niche model predicting lionfish abundance as a function of salinity.
The red lionfish, Pterois volitans, has beautiful red stripes, streaming fins, and a fearless disposition, and it is deadly. Native to the Pacific Ocean, the red lionfish was first discovered on coral reefs in the Bahamas in 1985. The species has spread to over 3 million square kilometers of the western Atlantic and Gulf of America (Gulf of Mexico). Lionfish have a voracious appetite for native fish, are armed with venomous spines, and have no natural predators in their new range.
DNA studies suggest that the lionfish invasion began with just a few females released off the coast of Florida, probably from a fish tank. Based on your knowledge of ocean currents, predict the direction in which the lionfish dispersed most quickly.
