What determines the primary structure of a DNA molecule? a. stem-and-loop configuration b. complementary base pairing c. deoxyribonucleotide sequence d. hydrophobic interactions and hydrogen bonding
Ch.4 - Nucleic Acids and the RNA World
Chapter 4, Problem 1
What are the four nitrogenous bases found in RNA? a. cytosine, guanine, thymine, uracil (C, G, T, U) b. adenine, cytosine, guanine, thymine (A, C, G, T) c. adenine, cytosine, guanine, uracil (A, C, G, U) d. alanine, cysteine, glycine, threonine (A, C, G, T)
 Verified step by step guidance
Verified step by step guidance1
Identify the correct nitrogenous bases that are components of RNA.
Eliminate options that include thymine (T) as it is a DNA base, not found in RNA.
Eliminate options that include amino acids (alanine, cysteine, glycine, threonine) as they are not nitrogenous bases.
Recognize that uracil (U) replaces thymine in RNA, indicating the presence of adenine (A), cytosine (C), guanine (G), and uracil (U) in RNA.
Select the option that lists all and only the bases found in RNA: adenine, cytosine, guanine, uracil (A, C, G, U).

Verified Solution
Video duration:
59sWas this helpful?
Key Concepts
Here are the essential concepts you must grasp in order to answer the question correctly.
Nitrogenous Bases
Nitrogenous bases are organic molecules that contain nitrogen and are fundamental components of nucleic acids, such as DNA and RNA. In RNA, the four nitrogenous bases are adenine (A), cytosine (C), guanine (G), and uracil (U). These bases pair with each other to form the genetic code, with adenine pairing with uracil in RNA, unlike DNA where adenine pairs with thymine.
Recommended video:
Guided course

5 Nitrogenous Bases
RNA Structure
RNA, or ribonucleic acid, is a single-stranded molecule that plays a crucial role in coding, decoding, regulation, and expression of genes. Unlike DNA, which contains thymine, RNA contains uracil as one of its nitrogenous bases. The structure of RNA allows it to perform various functions, including serving as a template for protein synthesis during translation.
Recommended video:
Guided course
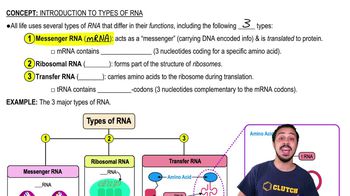
Introduction to Types of RNA
Base Pairing Rules
Base pairing rules dictate how nitrogenous bases pair with each other in nucleic acids. In RNA, adenine pairs with uracil, while cytosine pairs with guanine. Understanding these pairing rules is essential for grasping how genetic information is stored and transmitted, as they determine the complementary relationships between bases in the RNA sequence.
Recommended video:
Guided course

Chargaff's Rules
Related Practice
Textbook Question
1072
views
Textbook Question
Evaluate the following statements related to the synthesis of nucleic acids. Select True or False for each statement. T/F Ribonucleotides are added to the 3′ end of a DNA strand. T/F Polymerization of nucleic acids occurs by the formation of phosphodiester bonds. T/F Complementary pairing between sugars is required for copying nucleic acids. T/F Strands in a double helix are synthesized in an antiparallel orientation.
951
views
Textbook Question
Single strands of nucleic acids are directional, meaning that there are two different ends. What functional groups define the two different ends of a strand?
1579
views
