The most important primary producers in marine ecosystems are .
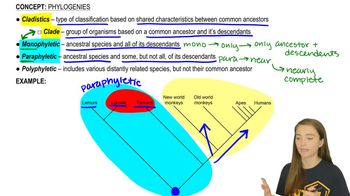
Why are protists considered paraphyletic? a. They include many extinct forms, including lineages that no longer have any living representatives. b. They include some but not all descendants of their most recent common ancestor. c. They represent all of the descendants of a single common ancestor. d. Not all protists have all of the synapomorphies that define the Eukarya, such as a nucleus.
 Verified step by step guidance
Verified step by step guidance
Verified video answer for a similar problem:
Key Concepts
Paraphyly
Eukarya

Synapomorphies
Evaluate the following statements regarding motility in protists. Select True or False for each statement. T/F Amoeboid motion is common in species with cell walls. T/F Some protists use flagella to swim. T/F Some protists use cilia to swim, which are shorter and more numerous than flagella. T/F Amoeboid motion requires ATP and interactions between the proteins actin and myosin.
How can dinoflagellates be harmful to humans? a. They are transmitted by mosquitoes and cause malaria. b. They produce toxins that can be absorbed by clams and other shellfish which, when eaten by people, can lead to paralytic shellfish poisoning. c. They cause amoebic dysentery which leads to severe diarrhea and dehydration. d. They are transmitted by tsetse flies and cause 'sleeping sickness.'
