Imagine discovering a loss-of-function mutation in a eukaryotic gene. You determine the gene's nucleotide sequence from the start site for transcription to the termination point of transcription and find no differences from the wild-type sequence. Explain where you think the mutation might be and how the mutation might be acting.
Explain what's wrong with this statement: All point mutations change the genotype and the phenotype.

Verified Solution
Key Concepts
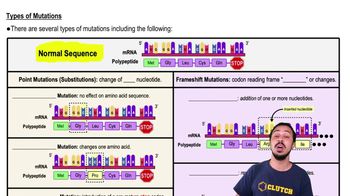
Point Mutations

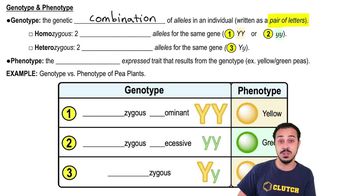
Genotype vs. Phenotype
Silent Mutations
Which of the following describes mutations? Select True or False for each statement. T/F Point mutations can occur in any DNA sequence. T/F Frameshift mutations can occur in any DNA sequence. T/F Neutral mutations depend on the degeneracy of the genetic code. T/F Deleterious mutations occur only in protein-coding sequences of DNA.
In a particular bacterial species, temperature-sensitive conditional mutations cause expression of a wild-type phenotype at one growth temperature and a mutant phenotype at another—typically higher—temperature. Imagine that when a bacterial cell carrying such a mutation is shifted from low to high growth temperatures, RNA polymerases in the process of elongation complete transcription normally, but no new transcripts can be started. The mutation in this strain most likely affects: a. the terminator sequence b. the start codon c. sigma d. one of the polypeptides of the core RNA polymerase
In what ways are a promoter and a start codon similar? In what ways are they different?
The nucleotide shown here is called cordycepin triphosphate. It is a natural product of a fungus that is used in traditional medicines. If cordycepin triphosphate is added to a cell-free transcription reaction, the nucleotide is added onto the growing RNA chain but then no more nucleotides can be added. Examine the structure of cordycepin and explain why it ends transcription.
Draw a hypothetical metabolic pathway in Neurospora crassa composed of five substrates, five enzymes, and a product called nirvana. Number the substrates 1–5, and label the enzymes A–E, in order. (For instance, enzyme A catalyzes the reaction between substrates 1 and 2.) (a) Suppose a mutation made the gene for enzyme C nonfunctional. What molecule would accumulate in the affected cells?
