Here are the essential concepts you must grasp in order to answer the question correctly.
Homologous Chromosomes
Homologous chromosomes are pairs of chromosomes in a diploid organism that have the same structure, size, and gene content. One chromosome of each pair is inherited from each parent, and they carry the same genes at the same loci, although the alleles (versions of the genes) may differ. This similarity is crucial for processes like meiosis, where homologous chromosomes pair up and exchange genetic material.
Recommended video:
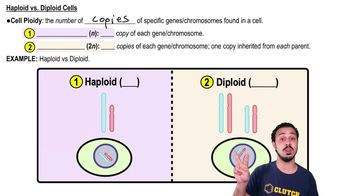
Diploid Cells
Diploid cells contain two complete sets of chromosomes, one from each parent, represented as 2n. In humans, for example, diploid cells have 46 chromosomes, organized into 23 homologous pairs. This diploid state is essential for sexual reproduction, as it allows for genetic diversity through the combination of maternal and paternal genes during fertilization.
Recommended video:
Haploid vs. Diploid Cells
Chromatids
Chromatids are the two identical halves of a replicated chromosome, which are joined together at a region called the centromere. During cell division, specifically mitosis and meiosis, chromatids separate to ensure that each daughter cell receives an identical set of chromosomes. While chromatids are crucial for understanding chromosome behavior during division, they are not the same as homologous chromosomes, which refer to the paired chromosomes themselves.
Recommended video:
Eukaryotic Chromatin Modifications