According to Hamilton's rule, a. natural selection does not favor altruistic behavior that causes the death of the altruist. b. natural selection favors altruistic acts when the resulting benefit to the recipient, corrected for relatedness, exceeds the cost to the altruist. c. natural selection is more likely to favor altruistic behavior that benefits an offspring than altruistic behavior that benefits a sibling. d. the effects of kin selection are larger than the effects of direct natural selection on individuals.
Although many chimpanzees live in environments with oil palm nuts, members of only a few populations use stones to crack open the nuts. The likely explanation is that a. the behavioral difference is caused by genetic differences between populations. b. members of different populations have different nutritional requirements. c. the cultural tradition of using stones to crack nuts has arisen in only some populations. d. members of different populations differ in learning ability.
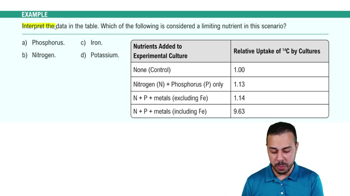
 Verified step by step guidance
Verified step by step guidance
Verified video answer for a similar problem:
Key Concepts
Cultural Transmission
Genetic Variation

Nutritional Ecology

Female spotted sandpipers aggressively court males and, after mating, leave the clutch of young for the male to incubate. This sequence may be repeated several times with different males until no available males remain, forcing the female to incubate her last clutch. Which of the following terms best describes this behavior? a. polygyny b. polyandry c. promiscuity d. certainty of paternity
A region of the canary forebrain shrinks during the nonbreeding season and enlarges when breeding season begins. This change is probably associated with the annual a. addition of new syllables to a canary's song repertoire. b. crystallization of subsong into adult songs. c. sensitive period in which canary parents imprint on new offspring. d. elimination of the memorized template for songs sung the previous year.
Which of the following is not required for a behavioral trait to evolve by natural selection? a. In each individual, the form of the behavior is determined entirely by genes. b. The behavior varies among individuals. c. An individual's reproductive success depends in part on how the behavior is performed. d. Some component of the behavior is genetically inherited.
