Here are the essential concepts you must grasp in order to answer the question correctly.
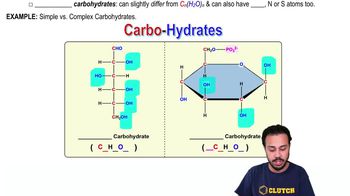
Carbohydrates
Carbohydrates are organic compounds made up of carbon, hydrogen, and oxygen, typically in a ratio of 1:2:1. They are classified into three main categories: monosaccharides, disaccharides, and polysaccharides. Carbohydrates serve as a primary energy source for living organisms and play crucial roles in cellular structure and function.
Recommended video:
Disaccharides
Disaccharides are carbohydrates formed by the combination of two monosaccharide molecules through a glycosidic bond. Common examples include sucrose (table sugar) and lactose (milk sugar). Disaccharides are important for energy storage and transport in organisms, but they are less complex than polysaccharides.
Recommended video:
Formation & Breakdown of Polysaccharides
Polysaccharides
Polysaccharides are large, complex carbohydrates composed of long chains of monosaccharide units linked together. They serve various functions, including energy storage (e.g., starch and glycogen) and structural support (e.g., cellulose in plant cell walls). Polysaccharides encompass both disaccharides and simpler sugars, making them a broader category.
Recommended video:
Formation & Breakdown of Polysaccharides