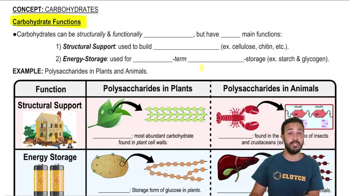
Textbook Question
Which of the following is not a major activity of the stomach?
a. Storage
b. HCl production
c. Nutrient absorption
d. Enzyme secretion
1644
views

 Verified step by step guidance
Verified step by step guidance

Which of the following is not a major activity of the stomach?
a. Storage
b. HCl production
c. Nutrient absorption
d. Enzyme secretion
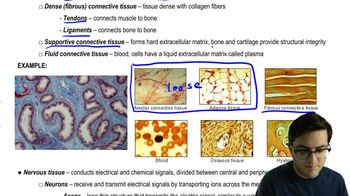
If you put the following events in the order they occur in the human digestive system, the third event in the series would be
a. Cells in gastric pits secrete protons.
b. Pepsin activates pepsinogen.
c. HCl activates pepsinogen.
d. Partially digested food enters the small intestine.
After surgical removal of the gallbladder, a person might need to limit his or her dietary intake of
a. Starch
b. Protein
c. Sugar
d. Fat