Photosynthesis ceases when leaves wilt, mainly because a. the chlorophyll in wilting leaves is degraded. b. accumulation of CO2 in the leaf inhibits enzymes. c. stomata close, preventing CO2 from entering the leaf. d. photolysis, the water-splitting step of photosynthesis, cannot occur when there is a water deficiency.
Ch. 36 - Resource Acquisition and Transport in Vascular Plants
All textbooks Campbell 11th Edition
Campbell 11th Edition Ch. 36 - Resource Acquisition and Transport in Vascular Plants
Ch. 36 - Resource Acquisition and Transport in Vascular Plants Problem 7
Problem 7
 Campbell 11th Edition
Campbell 11th Edition Ch. 36 - Resource Acquisition and Transport in Vascular Plants
Ch. 36 - Resource Acquisition and Transport in Vascular Plants Problem 7
Problem 7Chapter 36, Problem 7
Compared with a cell with few aquaporin proteins in its membrane, a cell containing many aquaporin proteins will a. have a faster rate of osmosis. b. have a lower water potential. c. have a higher water potential. d. accumulate water by active transport.
 Verified step by step guidance
Verified step by step guidance1
Understand the role of aquaporin proteins: Aquaporins are integral membrane proteins that form pores in the cell membrane, specifically facilitating the transport of water molecules across the membrane.
Relate aquaporins to osmosis: Osmosis is the movement of water across a semipermeable membrane from an area of lower solute concentration to an area of higher solute concentration. Aquaporins increase the permeability of the cell membrane to water, thus potentially increasing the rate of osmosis.
Analyze the options: Option (a) suggests that more aquaporins lead to a faster rate of osmosis, which aligns with the function of aquaporins as they facilitate water movement. Options (b) and (c) discuss water potential, which is influenced by solute concentration rather than the number of aquaporins. Option (d) is incorrect because water movement through aquaporins is passive, not active transport.
Eliminate incorrect answers: Since aquaporins facilitate passive water movement and do not affect solute concentration directly, options (b), (c), and (d) can be eliminated. Water potential is not directly altered by the number of aquaporins, and water is not accumulated by active transport through aquaporins.
Choose the correct answer: Based on the understanding of aquaporins and osmosis, the correct answer is (a) have a faster rate of osmosis, as more aquaporins increase the cell's permeability to water, thereby potentially increasing the rate at which osmosis occurs.

Verified Solution
Video duration:
50sWas this helpful?
Key Concepts
Here are the essential concepts you must grasp in order to answer the question correctly.
Aquaporins
Aquaporins are specialized channel proteins embedded in cell membranes that facilitate the rapid transport of water molecules in and out of cells. They play a crucial role in regulating water balance and are essential for processes such as osmosis, where water moves across a semipermeable membrane. The presence of more aquaporins increases the permeability of the membrane to water, enhancing the rate of osmosis.
Recommended video:
Guided course
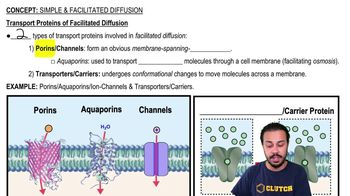
Transport Proteins of Facilitated Diffusion
Osmosis
Osmosis is the passive movement of water molecules through a selectively permeable membrane from an area of lower solute concentration to an area of higher solute concentration. This process continues until equilibrium is reached, and it is driven by the difference in water potential. The rate of osmosis can be significantly influenced by the number of aquaporins present in the membrane.
Recommended video:
Guided course
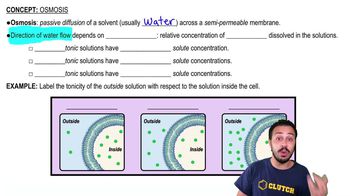
Osmosis
Water Potential
Water potential is a measure of the potential energy of water in a system and determines the direction of water movement. It is influenced by solute concentration and pressure; a higher solute concentration results in lower water potential. Cells with many aquaporins can maintain a higher water potential by allowing more water to enter, thus affecting the overall osmotic balance within the cell.
Recommended video:
Guided course

Water Potential
Related Practice
Textbook Question
1204
views
Textbook Question
What would enhance water uptake by a plant cell? a. decreasing the Ψ of the surrounding solution b. positive pressure on the surrounding solution c. the loss of solutes from the cell d. increasing the Ψ of the cytoplasm
772
views
Textbook Question
A plant cell with a ΨS of −0.65 MPa maintains a constant volume when bathed in a solution that has a ΨS of −0.30 MPa and is in an open container. The cell has a a. ΨP of +0.65 MPa. b. Ψ of −0.65 MPa. c. ΨP of +0.35 MPa. d. ΨP of 0 MPa.
696
views
Textbook Question
Which of the following would tend to increase transpiration? a. spiny leaves b. sunken stomata c. a thicker cuticle d. higher stomatal density
1305
views