Textbook Question
One of the characteristics unique to animals is a. gastrulation. b. multicellularity. c. sexual reproduction. d. flagellated sperm.
1102
views
1
rank
 Verified step by step guidance
Verified step by step guidance
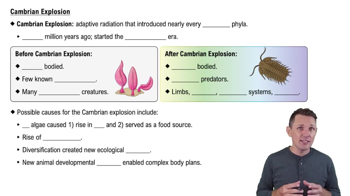
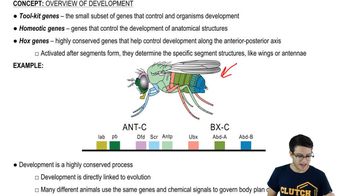

One of the characteristics unique to animals is a. gastrulation. b. multicellularity. c. sexual reproduction. d. flagellated sperm.
The distinction between sponges and other animal phyla is based mainly on the absence versus the presence of a. a body cavity. b. a complete digestive tract. c. mesoderm. d. tissues.
Based on the tree in Figure 32.11, which statement is false? a. The animal kingdom is monophyletic. b. Acoelomate flatworms are more closely related to echinoderms than to annelids. c. Sponges are basal animals. d. Bilaterians form a clade