Here are the essential concepts you must grasp in order to answer the question correctly.
Transcription Factors
Transcription factors are proteins that bind to specific DNA sequences, facilitating the recruitment of RNA polymerase to the promoter region of a gene. They play a crucial role in regulating gene expression by either promoting or inhibiting the transcription process. In eukaryotic cells, the binding of multiple transcription factors is essential for the initiation of transcription.
Recommended video:
Introduction to Transcription Factors
Promoter Region
The promoter region is a specific sequence of DNA located upstream of a gene that serves as the binding site for RNA polymerase and transcription factors. It contains essential elements that determine the start site of transcription and the efficiency of gene expression. The proper exposure and recognition of the promoter are critical for the initiation of transcription in eukaryotic cells.
Recommended video:
Terrestrial Biomes: Northern Regions Example 1
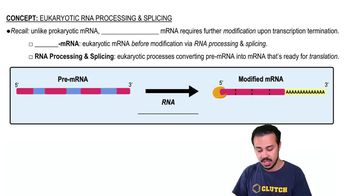
Eukaryotic Transcription Process
In eukaryotic cells, transcription is a multi-step process that involves the synthesis of RNA from a DNA template. This process requires the unwinding of DNA, the assembly of transcription factors and RNA polymerase at the promoter, and the elongation of the RNA strand. Unlike prokaryotes, eukaryotic transcription also involves post-transcriptional modifications, such as capping and splicing, before the mRNA is translated.
Recommended video:
Eukaryotic RNA Processing and Splicing