Here are the essential concepts you must grasp in order to answer the question correctly.
Punnett Square
A Punnett square is a diagram used in genetics to predict the genotypes of offspring from a cross between two parents. It organizes the possible combinations of alleles from each parent, allowing for a visual representation of genetic variation. By filling in the square with the alleles, one can easily determine the potential genotypes and phenotypes of the offspring.
Recommended video:
Heterozygous
Heterozygous refers to an organism that has two different alleles for a particular gene, one inherited from each parent. In the context of the pea plants, being heterozygous for pod color and shape means that each plant carries one dominant and one recessive allele for these traits. This genetic variation is crucial for understanding the potential outcomes of the cross.
Recommended video:
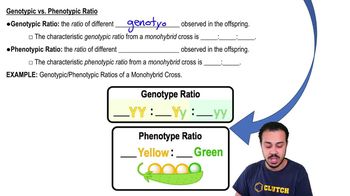
Phenotypic Ratio
The phenotypic ratio is the ratio of different phenotypes (observable traits) that result from a genetic cross. It is derived from the genotypic ratios obtained from the Punnett square and indicates the likelihood of each phenotype appearing in the offspring. For example, in a dihybrid cross, the phenotypic ratio can reveal the expected distribution of traits such as pod color and shape.
Recommended video:
Genotypic vs. Phenotypic Ratio