Consider this pathway: epinephrine → G protein-coupled receptor → G protein → adenylyl cyclase → cAMP. Identify the second messenger.
a. cAMP
b. G protein
c. GTP
d. Adenylyl cyclase

 Verified step by step guidance
Verified step by step guidance

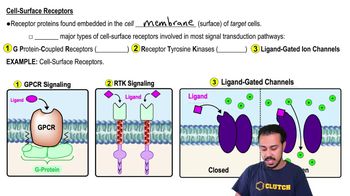

Consider this pathway: epinephrine → G protein-coupled receptor → G protein → adenylyl cyclase → cAMP. Identify the second messenger.
a. cAMP
b. G protein
c. GTP
d. Adenylyl cyclase
Apoptosis involves all but which of the following?
a. Fragmentation of the DNA
b. Cell-signaling pathways
c. Lysis of the cell
d. Digestion of cellular contents by scavenger cells
Which observation suggested to Sutherland the involvement of a second messenger in epinephrine's effect on liver cells?
a. Enzymatic activity was proportional to the amount of calcium added to a cell-free extract.
b. Receptor studies indicated that epinephrine was a ligand.
c. Glycogen breakdown was observed only when epinephrine was administered to intact cells.
d. Glycogen breakdown was observed only when epinephrine and glycogen phosphorylase were mixed.