The feeding relationships among the species in a community determine the community's
a. Secondary succession
b. Ecological niche
c. Species richness
d. Trophic structure

 Verified step by step guidance
Verified step by step guidance
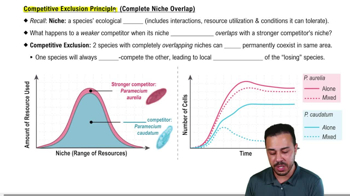
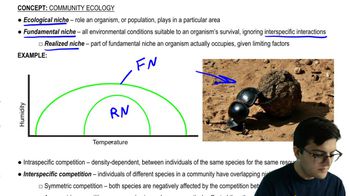

The feeding relationships among the species in a community determine the community's
a. Secondary succession
b. Ecological niche
c. Species richness
d. Trophic structure
Based on the intermediate disturbance hypothesis, a community's species diversity is increased by
a. Frequent massive disturbance
b. Stable conditions with no disturbance
c. Moderate levels of disturbance
d. Human intervention to eliminate disturbance
According to the island equilibrium model, species richness would be greatest on an island that is
a. Large and remote
b. Small and remote
c. Large and close to a mainland
d. Small and close to a mainland
Predators that are keystone species can maintain species diversity in a community if they
a. Competitively exclude other predators
b. Prey on the community's dominant species
c. Reduce the number of disruptions in the community
d. Prey only on the least abundant species in the community