The middle ear converts a. air pressure waves to fluid pressure waves. b. air pressure waves to nerve impulses. c. fluid pressure waves to nerve impulses. d. pressure waves to hair cell movements.
Ch. 50 - Sensory and Motor Mechanisms
Chapter 50, Problem 5
The transduction of sound waves into action potentials occurs a. in the tectorial membrane as it is stimulated by hair cells. b. when hair cells are bent against the tectorial membrane, causing them to depolarize and release neurotransmitter that stimulates sensory neurons. c. as the basilar membrane vibrates at different frequencies in response to the varying volume of sounds. d. within the middle ear as the vibrations are amplified by the malleus, incus, and stapes.

Verified Solution
Video duration:
45sWas this helpful?
Key Concepts
Here are the essential concepts you must grasp in order to answer the question correctly.
Hair Cells and Sound Transduction
Hair cells are specialized sensory cells located in the cochlea of the inner ear. They play a crucial role in converting sound waves into electrical signals. When sound waves cause the fluid in the cochlea to move, hair cells bend, leading to depolarization and the release of neurotransmitters that activate sensory neurons.
Recommended video:
Guided course
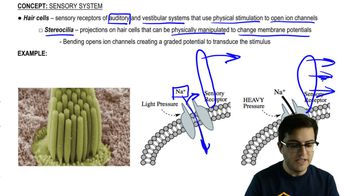
Hair Cells
Tectorial Membrane
The tectorial membrane is a gelatinous structure in the cochlea that sits above the hair cells. When sound waves cause the basilar membrane to vibrate, the movement of the basilar membrane causes the hair cells to bend against the tectorial membrane. This bending is essential for initiating the process of sound transduction.
Recommended video:
Guided course

Biological Membranes
Basilar Membrane and Frequency Response
The basilar membrane is a flexible structure that runs along the length of the cochlea and responds to different sound frequencies. Higher frequencies cause vibrations near the base, while lower frequencies affect the apex. This frequency-specific vibration is critical for the perception of pitch and is integral to the auditory transduction process.
Recommended video:

Allele Frequencies
Related Practice
Textbook Question
819
views
Textbook Question
During the contraction of a vertebrate skeletal muscle fiber, calcium ions a. break cross-bridges as a cofactor in hydrolysis of ATP. b. bind with troponin, changing its shape so that the myosin-binding sites on actin are exposed. c. transmit action potentials from the motor neuron to the muscle fiber. d. spread action potentials through the T tubules.
545
views
Textbook Question
The human brain differentiates tastes from smells because action potentials for the two sensations differ in (A)magnitude and shape. (B)threshold potential. (C)where they are received in the brain. (D)how long they take to reach the brain.
836
views
