Here are the essential concepts you must grasp in order to answer the question correctly.
Anatomy of the Pharynx
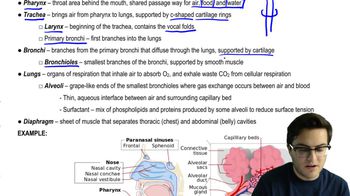
The pharynx is a muscular tube that serves as a passageway for both air and food. It connects the nasal cavity and mouth to the larynx and esophagus, playing a crucial role in the respiratory and digestive systems. Understanding its structure helps clarify how the trachea and esophagus branch from this common pathway.
Recommended video:
Function of the Trachea
The trachea, or windpipe, is a tube that carries air from the larynx to the bronchi of the lungs. It is lined with ciliated mucosa that helps trap and expel foreign particles. Recognizing its function is essential for understanding how it connects to the pharynx and its role in the respiratory system.
Recommended video:
Function of the Esophagus
The esophagus is a muscular tube that transports food from the pharynx to the stomach. It uses rhythmic contractions called peristalsis to move food downward. Understanding the esophagus's role in digestion is important for recognizing how it connects to the pharynx and differentiates from the trachea.
Recommended video: