Textbook Question
Which of the following is a characteristic that distinguishes gymnosperms and angiosperms from other plants?
a. Alternation of generations
b. Independent gametophytes
c. Vascular tissue
d. Ovules
2385
views

 Verified step by step guidance
Verified step by step guidance

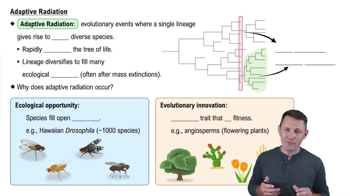
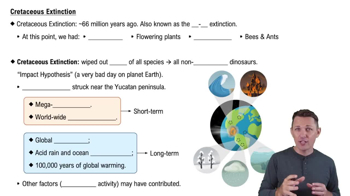
Which of the following is a characteristic that distinguishes gymnosperms and angiosperms from other plants?
a. Alternation of generations
b. Independent gametophytes
c. Vascular tissue
d. Ovules
Which of the following are present in angiosperms but not in gymnosperms?
A. seeds
B. pollen
C. ovaries
D. ovules
Use the letters a–d to label where on the phylogenetic tree each of the following derived characters appears.
a. Flowers
b. Embryos
c. Seeds
d. Vascular tissue