The largest unit within which gene flow can readily occur is a
a. Population.
b. Species.
c. Genus.
d. Hybrid.

 Verified step by step guidance
Verified step by step guidance

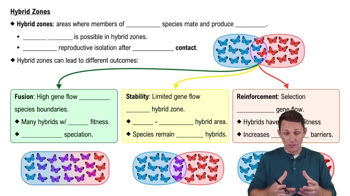

The largest unit within which gene flow can readily occur is a
a. Population.
b. Species.
c. Genus.
d. Hybrid.
Males of different species of the fruit fly Drosophila that live in the same parts of the Hawaiian Islands have different elaborate courtship rituals. These rituals involve fighting other males and making stylized movements that attract females. What type of reproductive isolation does this represent?
a. Habitat isolation
b. Temporal isolation
c. Behavioral isolation
d. Gametic isolation
According to the punctuated equilibria model:
a. Given enough time, most existing species will branch gradually into new species.
b. Most new species accumulate their unique features relatively rapidly as they come into existence, then change little for the rest of their duration as a species.
c. Most evolution occurs in sympatric populations.
d. Speciation is usually due to a single mutation.
Which of the following factors would be the most likely to contribute to allopatric speciation?
a. The separated population is large, and genetic drift occurs.
b. Selection pressures in the isolated population are similar to those in the ancestral population.
c. Gene flow between the two populations is extensive.
d. Different mutations begin to distinguish the gene pools of the separated populations.
Plant species A has a diploid chromosome number of 12. Plant species B has a diploid number of 16. A new species, C, arises as an allopolyploid from A and B. The diploid number for species C would probably be
a. 14
b. 16
c. 28
d. 56