Natural selection changes allele frequencies because some _________ survive and reproduce better than others. a. alleles b. loci c. species d. individuals
If the nucleotide variability of a locus equals 0%, what is the gene variability and number of alleles at that locus? a. gene variability=0%; number of alleles=0 b. gene variability=0%; number of alleles=1 c. gene variability=0%; number of alleles=2 d. gene variability>0%; number of alleles=2

Verified Solution
Key Concepts
Nucleotide Variability
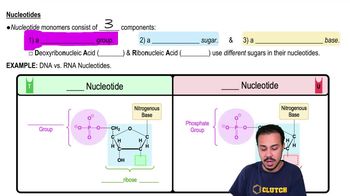
Gene Variability

Alleles

No two people are genetically identical, except for identical twins. The main source of genetic variation among humans is a. new mutations that occurred in the preceding generation. b. genetic drift. c. the reshuffling of alleles in sexual reproduction. d. environmental effects.
There are 25 individuals in population 1, all with genotype AA, and there are 40 individuals in population 2, all with genotype aa. Assume that these populations are located far from each other and that their environmental conditions are very similar. Based on the information given here, the observed genetic variation most likely resulted from a. genetic drift. b. gene flow. c.nonrandom mating. d. directional selection.
A fruit fly population has a gene with two alleles, A1 and A2. Tests show that 70% of the gametes produced in the population contain the A1 allele. If the population is in Hardy-Weinberg equilibrium, what proportion of the flies carry both A1 and A2? a. 0.7 b. 0.49 c. 0.42 d. 0.21
