Pseudohypertrophic muscular dystrophy is an inherited disorder that causes gradual deterioration of the muscles. It is seen almost exclusively in boys born to apparently unaffected parents and usually results in death in the early teens. Is this disorder caused by a dominant or a recessive allele? Is its inheritance sex-linked or autosomal? How do you know? Explain why this disorder is almost never seen in girls.
A man with hemophilia (a recessive, sex-linked condition) has a daughter without the condition. She marries a man who does not have hemophilia. What is the probability that their daughter will have hemophilia? Their son? If they have four sons, what is the probability that all will be affected?
 Verified step by step guidance
Verified step by step guidance
Verified Solution
Key Concepts
Hemophilia and Sex-Linked Inheritance

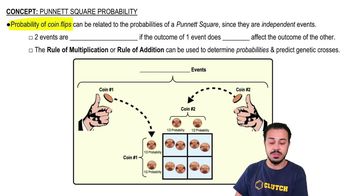
Punnett Square and Probability
Independent Assortment and Probability of Multiple Offspring

A wild-type fruit fly (heterozygous for gray body color and normal wings) is mated with a black fly with vestigial wings. The offspring have the following phenotypic distribution: wild-type, 778; black vestigial, 785; black normal, 158; gray vestigial, 162. What is the recombination frequency between these genes for body color and wing size? Is this consistent with the results of the experiment in Figure 15.9? Draw the chromosomes in the wild-type and black parents.
A planet is inhabited by creatures that reproduce with the same hereditary patterns seen in humans. Three phenotypic characters are height (T=tall, t=dwart), head appendages (A=antennae, a=no antennae), and nose morphology (S=upturned snout, s=downturned snout). Since the creatures are not 'intelligent,' Earth scientists are able to do some controlled breeding experiments using various heterozygotes in testcrosses. For tall heterozygotes with antennae, the offspring are tall antennae, 46; dwarf antennae, 7; dwarf no antennae, 42; tall no antennae, 5. For heterozygotes with antennae and an upturned snout, the offspring are antennae upturned snout, 47; antennae downturned snout, 2; no antennae downturned snout, 48; no antennae upturned snout, 3. Calculate the recombination frequencies for both experiments.
