Consider this pathway: epinephrine → G protein-coupled receptor → G protein → adenylyl cyclase → cAMP. Identify the second messenger. a. cAMP b. G protein c. GTP d. adenylyl cyclase
Ch. 11 - Cell Communication
Chapter 11, Problem 7
Protein phosphorylation is commonly involved with which of the following?
A. ligand binding by receptor tyrosine kinases.
B. activation of G protein-coupled receptors.
C. activation of protein kinase molecules.
D. release of Ca2+ from the ER lumen.
 Verified step by step guidance
Verified step by step guidance1
Identify the common processes in cellular signaling and regulation where protein phosphorylation plays a critical role.
Understand the role of receptor tyrosine kinases (RTKs) and how they function upon ligand binding. RTKs are known to autophosphorylate, which is a key step in their activation.
Examine the mechanism of G protein-coupled receptors (GPCRs) activation and how it leads to the activation of different types of proteins, but focus on whether phosphorylation is directly involved in their initial activation.
Analyze how protein kinase molecules are involved in phosphorylation and what activates these kinases. Consider the role of phosphorylation in activating or deactivating these enzymes.
Consider the process of calcium release from the endoplasmic reticulum (ER) and determine if phosphorylation directly influences this specific event.
Key Concepts
Here are the essential concepts you must grasp in order to answer the question correctly.
Protein Phosphorylation
Protein phosphorylation is a biochemical process that involves the addition of a phosphate group to a protein, typically mediated by enzymes known as kinases. This modification can alter the protein's function, activity, localization, or interaction with other molecules, playing a crucial role in cellular signaling and regulation.
Recommended video:
Guided course

Types of Phosphorylation
Receptor Tyrosine Kinases (RTKs)
Receptor tyrosine kinases are a class of cell surface receptors that, upon binding to a ligand, undergo dimerization and autophosphorylation on tyrosine residues. This phosphorylation activates downstream signaling pathways that regulate various cellular processes, including growth, differentiation, and metabolism.
Recommended video:
Guided course
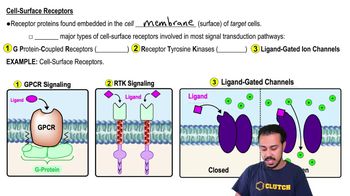
Cell-Surface Receptors
G Protein-Coupled Receptors (GPCRs)
G protein-coupled receptors are a large family of membrane receptors that play a key role in transmitting signals from outside the cell to the inside. When a ligand binds to a GPCR, it activates associated G proteins, which then trigger various intracellular signaling cascades, often involving phosphorylation events that modulate cellular responses.
Recommended video:
Guided course

Cell-Surface Receptors
Related Practice
Textbook Question
1863
views
Textbook Question
Apoptosis involves all but which of the following? a. fragmentation of the DNA b. cell-signaling pathways c. lysis of the cell d. digestion of cellular contents by scavenger cells
1264
views
Textbook Question
Which observation suggested to Sutherland the involvement of a second messenger in epinephrine's effect on liver cells? a. Enzymatic activity was proportional to the amount of calcium added to a cell-free extract. b. Receptor studies indicated that epinephrine was a ligand. c. Glycogen breakdown was observed only when epinephrine was administered to intact cells. d. Glycogen breakdown was observed only when epinephrine and glycogen phosphorylase were mixed.
1033
views
