The activation of receptor tyrosine kinases is characterized by a. dimerization and phosphorylation. b. dimerization and IP3 binding. c. a phosphorylation cascade. d. GTP hydrolysis.
Ch. 11 - Cell Communication
Chapter 11, Problem 1
Binding of a signaling molecule to which type of receptor leads directly to a change in the distribution of substances on opposite sides of the membrane? a. intracellular receptor b. G protein-coupled receptor c. phosphorylated receptor tyrosine kinase dimer d. ligand-gated ion channel
 Verified step by step guidance
Verified step by step guidance1
Identify the type of receptors listed and understand their basic functions. Intracellular receptors typically bind to molecules that can cross the cell membrane and affect transcription directly. G protein-coupled receptors activate internal signaling pathways. Receptor tyrosine kinases, when phosphorylated, also initiate several signaling cascades.
Focus on the receptor that directly changes the distribution of ions or molecules across the membrane. This process usually involves the movement of substances into or out of the cell.
Consider the mechanism of a ligand-gated ion channel, which opens in response to the binding of a signaling molecule, allowing specific ions to flow through the membrane, thereby changing the ion concentration on either side of the membrane.
Compare this mechanism to the other options. Intracellular receptors and receptor tyrosine kinases influence gene expression and enzyme activation, respectively, rather than directly altering substance distribution across the membrane. G protein-coupled receptors indirectly influence cellular changes through secondary messengers rather than directly changing ion distribution.
Conclude that the correct answer is 'd. ligand-gated ion channel' because this type of receptor directly leads to a change in the distribution of substances across the membrane by allowing ions to pass through the membrane when the receptor is activated by a ligand.

Verified video answer for a similar problem:
This video solution was recommended by our tutors as helpful for the problem above.
Video duration:
1mWas this helpful?
Key Concepts
Here are the essential concepts you must grasp in order to answer the question correctly.
Signal Transduction
Signal transduction refers to the process by which a cell responds to external signals, such as hormones or neurotransmitters. This involves the binding of signaling molecules to specific receptors on the cell membrane, leading to a cascade of biochemical events that ultimately result in a cellular response. Understanding this concept is crucial for analyzing how different receptors function in cellular communication.
Recommended video:
Guided course
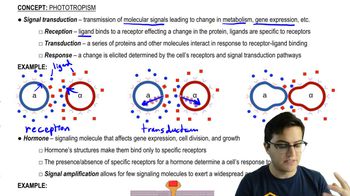
Signal Transduction and Response
Receptor Types
There are various types of receptors that mediate signal transduction, including intracellular receptors, G protein-coupled receptors, receptor tyrosine kinases, and ligand-gated ion channels. Each type has a distinct mechanism of action and effect on the cell. For instance, ligand-gated ion channels directly alter ion flow across the membrane, leading to immediate changes in cellular activity.
Recommended video:
Guided course

Intracellular Receptors
Membrane Potential and Ion Distribution
The distribution of ions across a cell membrane creates a membrane potential, which is essential for various cellular functions, including muscle contraction and nerve impulse transmission. Changes in ion distribution, often mediated by receptors like ligand-gated ion channels, can lead to rapid alterations in the cell's electrical state, influencing how the cell responds to stimuli.
Recommended video:
Guided course
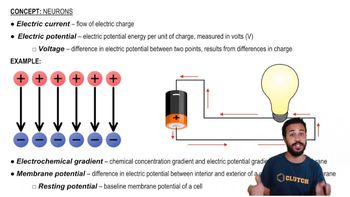
Membrane Potential
Related Practice
Textbook Question
1432
views
Textbook Question
Lipid-soluble signaling molecules, such as aldosterone, cross the membranes of all cells but affect only target cells because a. only target cells retain the appropriate DNA segments. b. intracellular receptors are present only in target cells. c. only target cells have enzymes that break down aldosterone. d. only in target cells is aldosterone able to initiate the phosphorylation cascade that turns genes on.
1559
views
Textbook Question
Consider this pathway: epinephrine → G protein-coupled receptor → G protein → adenylyl cyclase → cAMP. Identify the second messenger. a. cAMP b. G protein c. GTP d. adenylyl cyclase
1863
views
