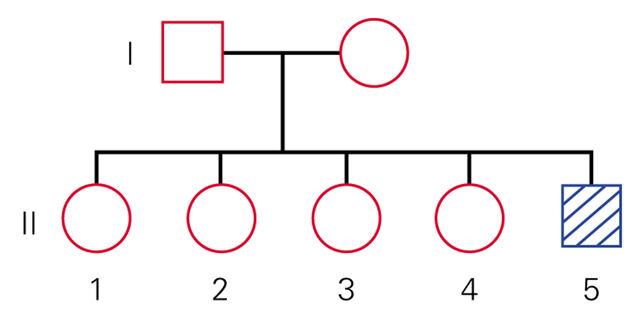
Textbook Question
When a trait is highly heritable, .
a. it is influenced by genes;
b. it is not influenced by the environment;
c. the variance of the trait in a population can be explained primarily by variance in genotypes;
d. A and C are correct;
e. A, B, and C are correct
848
views