Here are the essential concepts you must grasp in order to answer the question correctly.
Dominant and Recessive Alleles
In genetics, alleles can be classified as dominant or recessive. A dominant allele expresses its trait even when only one copy is present (heterozygous), while a recessive allele requires two copies (homozygous) to express its trait. Understanding this distinction is crucial for determining how genotypes relate to phenotypes in heritable diseases.
Recommended video:
Dominant vs. Recessive Alleles
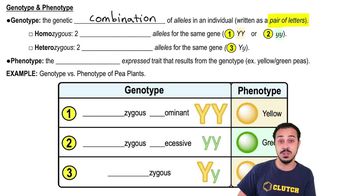
Genotype vs. Phenotype
Genotype refers to the genetic makeup of an individual, while phenotype is the observable expression of that genotype. An individual can carry a genotype that does not manifest as a disease phenotype due to the nature of the alleles involved, particularly in the case of recessive diseases where a single dominant allele can mask the effect of a recessive one.
Recommended video:
Heterozygous and Homozygous Conditions
Heterozygous individuals have two different alleles for a particular gene, while homozygous individuals have two identical alleles. In the context of heritable diseases, being heterozygous for a recessive disease means the individual carries one normal allele and one disease allele, which typically does not result in the disease phenotype, unlike homozygous conditions that often do.
Recommended video:
 Verified step by step guidance
Verified step by step guidance