Here are the essential concepts you must grasp in order to answer the question correctly.
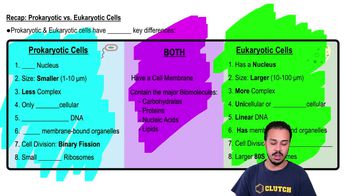
Prokaryotic vs. Eukaryotic Cells
Cells are classified into two main categories: prokaryotic and eukaryotic. Prokaryotic cells, which include bacteria and archaea, lack a nucleus and membrane-bound organelles, while eukaryotic cells, found in organisms like plants and animals, have a defined nucleus. The absence of a nucleus in the observed cells indicates they are prokaryotic.
Recommended video:
Recap: Prokaryotic vs. Eukaryotic Cells
Domains of Life
Life on Earth is categorized into three domains: Bacteria, Archaea, and Eukarya. Bacteria and Archaea are both prokaryotic, while Eukarya encompasses all eukaryotic organisms. Understanding these domains is crucial for identifying the type of cells being examined, especially when distinguishing between prokaryotic and eukaryotic characteristics.
Recommended video:
Microscopic Cell Examination
Microscopic examination of cells allows scientists to observe structural features that indicate their classification. The presence or absence of a nucleus, cell wall composition, and cell shape are key indicators. In this case, the observation of single cells without a nucleus suggests they are likely bacteria or archaea, guiding the identification process.
Recommended video:
 Verified step by step guidance
Verified step by step guidance