Here are the essential concepts you must grasp in order to answer the question correctly.
Meiosis
Meiosis is a specialized form of cell division that reduces the chromosome number by half, resulting in four haploid daughter cells. It consists of two sequential divisions: meiosis I and meiosis II. During meiosis I, homologous chromosomes are separated, while meiosis II separates sister chromatids. This process is essential for sexual reproduction, as it produces gametes with genetic diversity.
Recommended video:
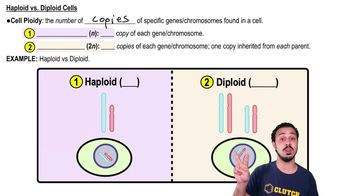
Haploid vs. Diploid
Haploid (n) cells contain one set of chromosomes, while diploid (2n) cells have two sets. In humans, somatic cells are diploid, containing 46 chromosomes, whereas gametes (sperm and egg) are haploid, containing 23 chromosomes. After meiosis I, the resulting daughter cells are haploid, as they have half the original chromosome number, which is crucial for maintaining chromosome number across generations during fertilization.
Recommended video:
Haploid vs. Diploid Cells
Sister Chromatids
Sister chromatids are identical copies of a single chromosome, formed during DNA replication. Each chromosome consists of two sister chromatids joined at a region called the centromere. During meiosis I, homologous chromosomes are separated, but sister chromatids remain together until meiosis II. Understanding the structure and behavior of sister chromatids is vital for grasping how genetic material is distributed during cell division.
Recommended video:
Eukaryotic Chromatin Modifications