Here are the essential concepts you must grasp in order to answer the question correctly.
Genetic Drift
Genetic drift is a mechanism of evolution that refers to random changes in allele frequencies within a population. It occurs due to chance events that can cause certain alleles to become more or less common, independent of natural selection. This phenomenon is particularly significant in small populations, where random events can have a larger impact on the genetic makeup of the population.
Recommended video:
Bottleneck Effect
The bottleneck effect is a specific type of genetic drift that occurs when a population undergoes a dramatic reduction in size due to environmental events or human activities. This reduction can lead to a loss of genetic diversity, as only a small number of individuals contribute to the gene pool. The surviving population may have different allele frequencies compared to the original population, which can significantly alter the evolutionary trajectory.
Recommended video:
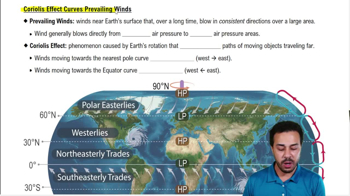
Coriolis Effect Curves Prevailing Winds
Founder Effect
The founder effect is another form of genetic drift that occurs when a small group of individuals establishes a new population in a different location. This small founding population may carry only a limited genetic variation from the original population, leading to different allele frequencies. As the new population grows, the genetic characteristics of the founders can have a lasting impact on the population's evolution, often resulting in reduced genetic diversity.
Recommended video:
Coriolis Effect Curves Prevailing Winds