Here are the essential concepts you must grasp in order to answer the question correctly.
Hypothesis Testing
Hypothesis testing is a statistical method used to determine the validity of a proposed explanation or prediction. In this context, the hypothesis suggests that eating chicken noodle soup can influence the duration or severity of colds. To test this hypothesis, one would compare the health outcomes of those who consume the soup against those who do not, looking for significant differences.
Recommended video:
Causation vs. Correlation
Causation refers to a direct cause-and-effect relationship between two variables, while correlation indicates a relationship without implying causation. The hypothesis implies that eating chicken noodle soup may cause a reduction in cold duration, which is a causal claim. Understanding this distinction is crucial for interpreting the results of any study related to the hypothesis.
Recommended video:
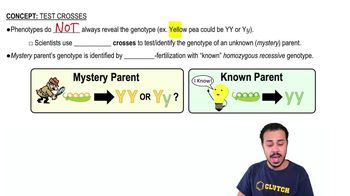
Dominant vs. Recessive Alleles
Control Groups
A control group is a baseline group in an experiment that does not receive the treatment being tested, allowing for comparison against the experimental group. In the context of the hypothesis, a control group would consist of individuals who do not consume chicken noodle soup, enabling researchers to assess the soup's effect on cold symptoms accurately. This helps to isolate the impact of the soup from other variables.
Recommended video:
 Verified step by step guidance
Verified step by step guidance