Types of Membrane Proteins exam Flashcards
 Back
BackTerms in this set (26)
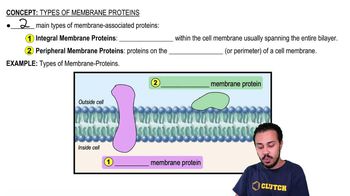
Integral membrane proteins
Proteins that are integrated or embedded within the cell membrane, usually spanning the entire phospholipid bilayer.
Peripheral membrane proteins
Proteins found on the periphery or perimeter of the biological membrane, not spanning the membrane.
Recognition
A function of membrane proteins where they mark a cell for identification.
Anchorage
A function of membrane proteins where they anchor the cell cytoskeleton to the extracellular matrix.
Transduction
A function of membrane proteins where they serve as receptors for signaling molecules, allowing for bio signaling.
Transport
A function of membrane proteins where they help with molecular transport across the membrane.
Linkage
A function of membrane proteins where they connect cells via protein linkages.
Enzymatic activity
A function of membrane proteins where they serve as enzymes to speed up chemical reactions.
What mnemonic can help remember the functions of membrane proteins?
The word 'RATTLE' helps remember the functions: Recognition, Anchorage, Transduction, Transport, Linkage, Enzymatic activity.
What is the role of membrane proteins in cell identification?
Membrane proteins mark cells for identification, helping distinguish one cell from another.
How do membrane proteins assist in signal transduction?
They serve as receptors for signaling molecules, allowing signals to affect the cell's metabolism.
What is the function of membrane proteins in molecular transport?
They help transport molecules across the cell membrane.
How do membrane proteins contribute to cell linkage?
They connect cells via protein linkages, forming cell junctions.
What is the significance of membrane proteins in enzymatic processes?
They serve as enzymes to speed up chemical reactions, facilitating various enzymatic processes.
Where are peripheral membrane proteins located?
On the surface of the biological membrane, either on the extracellular or intracellular side.
What is the integrated region of an integral membrane protein?
The part of the protein that spans the entire phospholipid bilayer.
What is the extracellular portion of a membrane protein?
The part of the protein that is located outside the cell.
What is the intracellular portion of a membrane protein?
The part of the protein that is located inside the cell.
What is the role of membrane proteins in the extracellular matrix?
They anchor the cell cytoskeleton to the extracellular matrix.
How do membrane proteins facilitate cell communication?
Through signal transduction, where they act as receptors for signaling molecules.
What is the function of membrane proteins in cell junctions?
They link cells together via protein linkages.
How do membrane proteins assist in chemical reactions?
By serving as enzymes that speed up the reactions.
What is the significance of the phospholipid bilayer in integral proteins?
Integral proteins span the entire phospholipid bilayer, integrating into the membrane.
What is the function of the intracellular portion of an integral protein?
It interacts with the inside of the cell, contributing to various cellular processes.
What is the function of the extracellular portion of an integral protein?
It interacts with the outside of the cell, playing a role in cell communication and signaling.
What is the role of membrane proteins in maintaining cellular integrity?
They perform various functions such as anchorage, transport, and linkage, which are crucial for cellular structure and function.