Types of Membrane Proteins definitions Flashcards
 Back
BackTypes of Membrane Proteins definitions
1/10
Terms in this set (10)
- ProteinsLarge biomolecules composed of amino acids, essential for cell structure, function, and regulation, often embedded in or associated with cell membranes.
- MembranesStructures composed of a phospholipid bilayer that form the boundary of cells and organelles, regulating the passage of substances and housing various proteins for communication and transport.
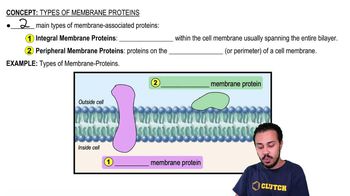
- Integral Membrane ProteinsProteins embedded within the cell membrane, often spanning the entire phospholipid bilayer, with regions exposed to both the intracellular and extracellular environments.
- Phospholipid BilayerA double-layered structure forming the core of cell membranes, composed of hydrophilic heads facing outward and hydrophobic tails inward, creating a selective barrier for molecules.
- ExtracellularLocated outside the cell membrane, this region interacts with the external environment and is crucial for communication, adhesion, and transport processes.
- IntracellularLocated within the cell, often referring to the environment or processes occurring inside the cell membrane.
- Peripheral Membrane ProteinsProteins located on the outer or inner surface of the cell membrane, not embedded within the lipid bilayer, and involved in various cellular functions like signaling and structural support.
- RibosomeA cellular structure that translates mRNA into polypeptides, facilitating protein synthesis.
- CytoskeletonA dynamic network of protein filaments providing structural support, shape, and facilitating intracellular transport and cellular movement.
- Extracellular MatrixA complex network of proteins and polysaccharides outside cells, providing structural support, segregating tissues, and regulating intercellular communication.